FRTE 1:1 Verification
These comments provided by Neurotechnology are based on NIST FRTE 1:1 Verification ongoing evaluation results reviewed on November 27, 2023.
NIST FRTE 1:1 Verification evaluates how well face recognition technologies work across various uses, from visa image checks to spotting duplicates in passports or identifying individuals in random photos. Eight testing scenarios range from simple dataset deduplication to real-life situations with cooperating and non-cooperating subjects. Algorithms' accuracy is the primary assessment metric, with additional metrics like matching speed and memory consumption. The datasets feature only one face per image.
See FRTE official page for more information.
The Face Recognition Technology Evaluation (FRTE) started in July, 2023, as a successor of the previous FRVT Ongoing evaluation of face verification algorithms. The FRTE 1:1 Verification track allows vendors to submit multiple algorithms once every three months, but the report takes into account only 2 latest submissions per vendor. Thus, only 539 algorithms are analyzed in the current results table from NIST.
Neurotechnology algorithm has been ranked in the top 3% of most accurate results for border control supervised (Visa Border, Border) and unsupervised (Border-Kiosk) scenarios among all submissions. The results for each scenario are presented below:
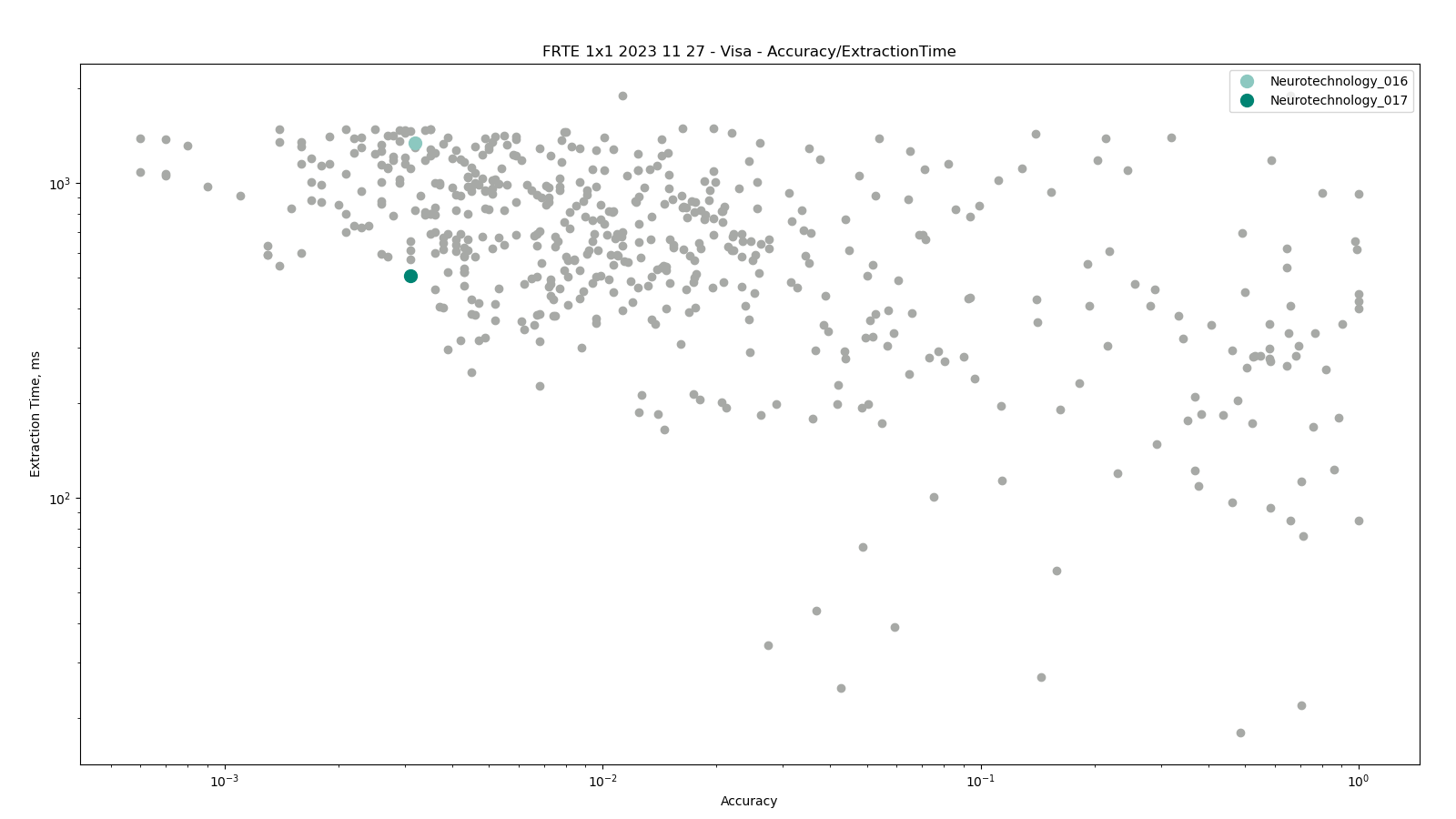
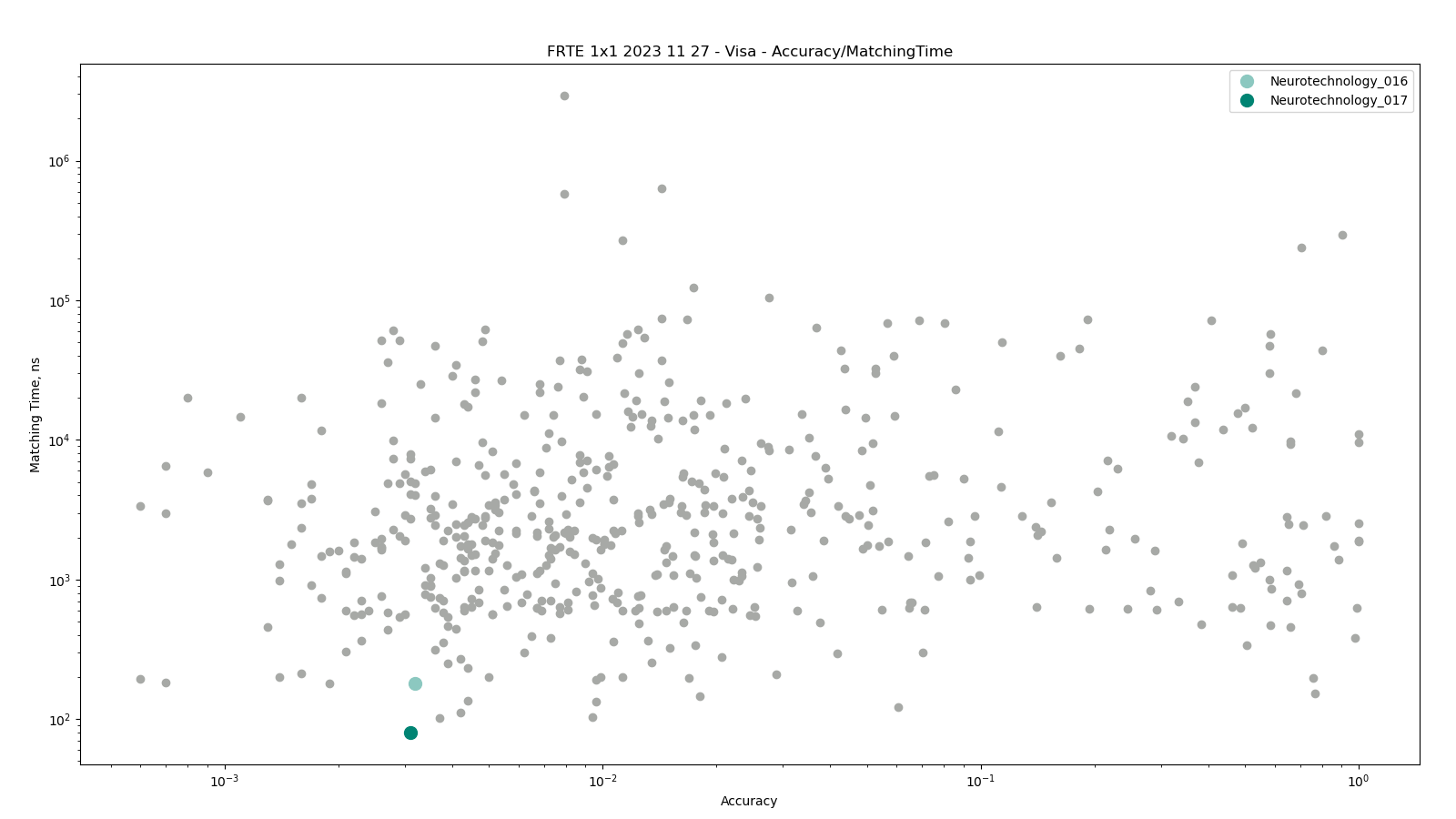
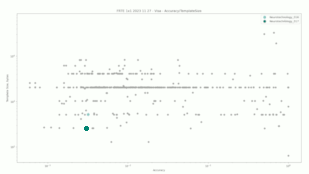
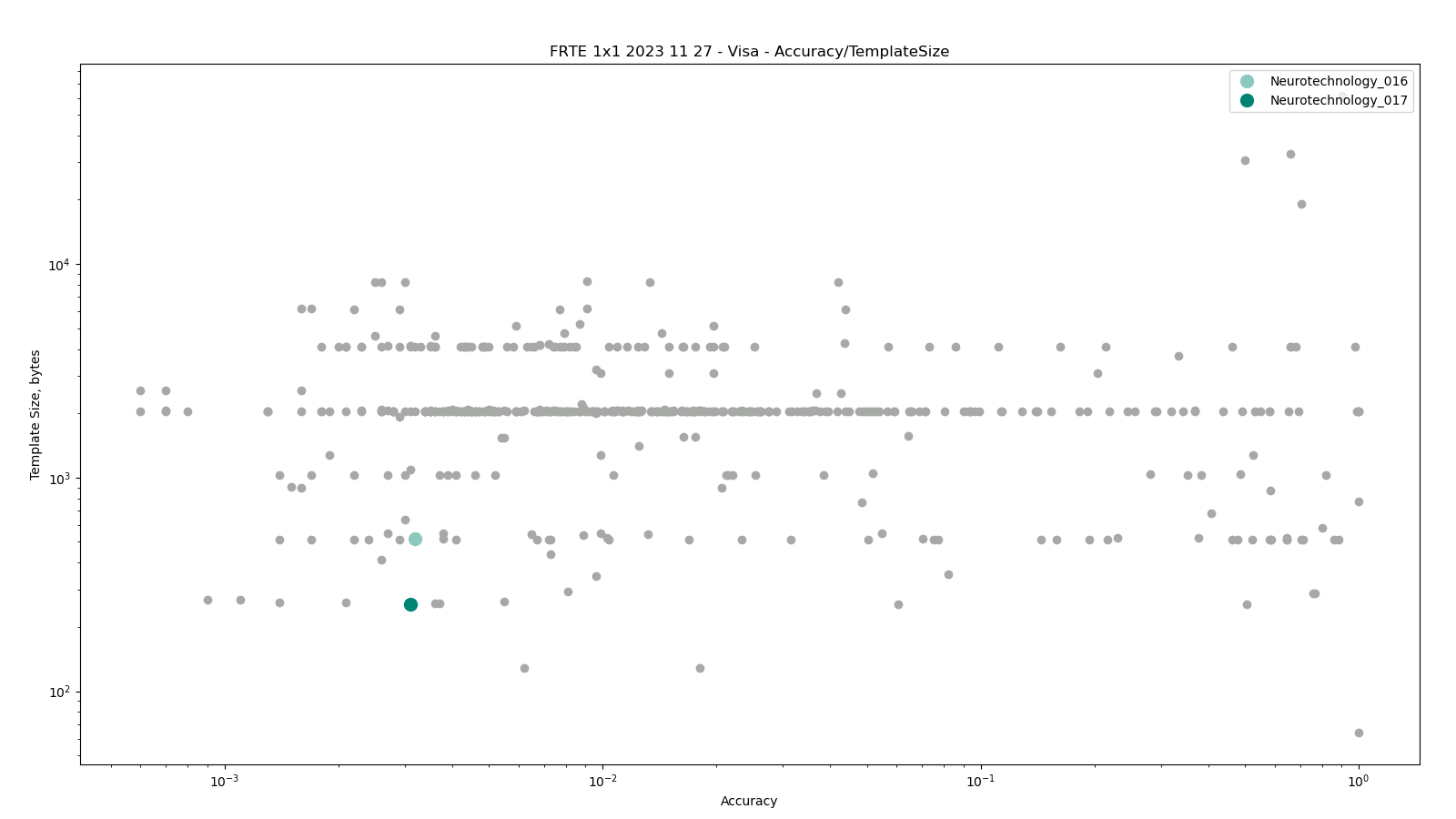
Visa
The comparisons were performed between all face templates from the VISA dataset.
Neurotechnology algorithm accuracy in this scenario was 0.31% FNMR at 0.0001% FMR. The most accurate contender showed 0.06% FNMR at the same FMR.
Scenario overview
- One image from the dataset was used to create one face template.
- All face templates were compared between each other.
- Each comparison score was obtained by comparing two different templates (simple one-to-one verification).
- The comparisons were fully zero-effort, meaning there was no pre-grouping by gender, age or other covariates.
Accuracy versus performance metrics
The charts below show the accuracy of all tested algorithms, with the highlighted dots corresponding to the Neurotechnology algorithm submissions.
Click to zoom
Click to zoom
Click to zoom
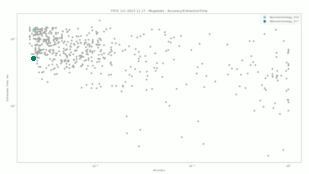
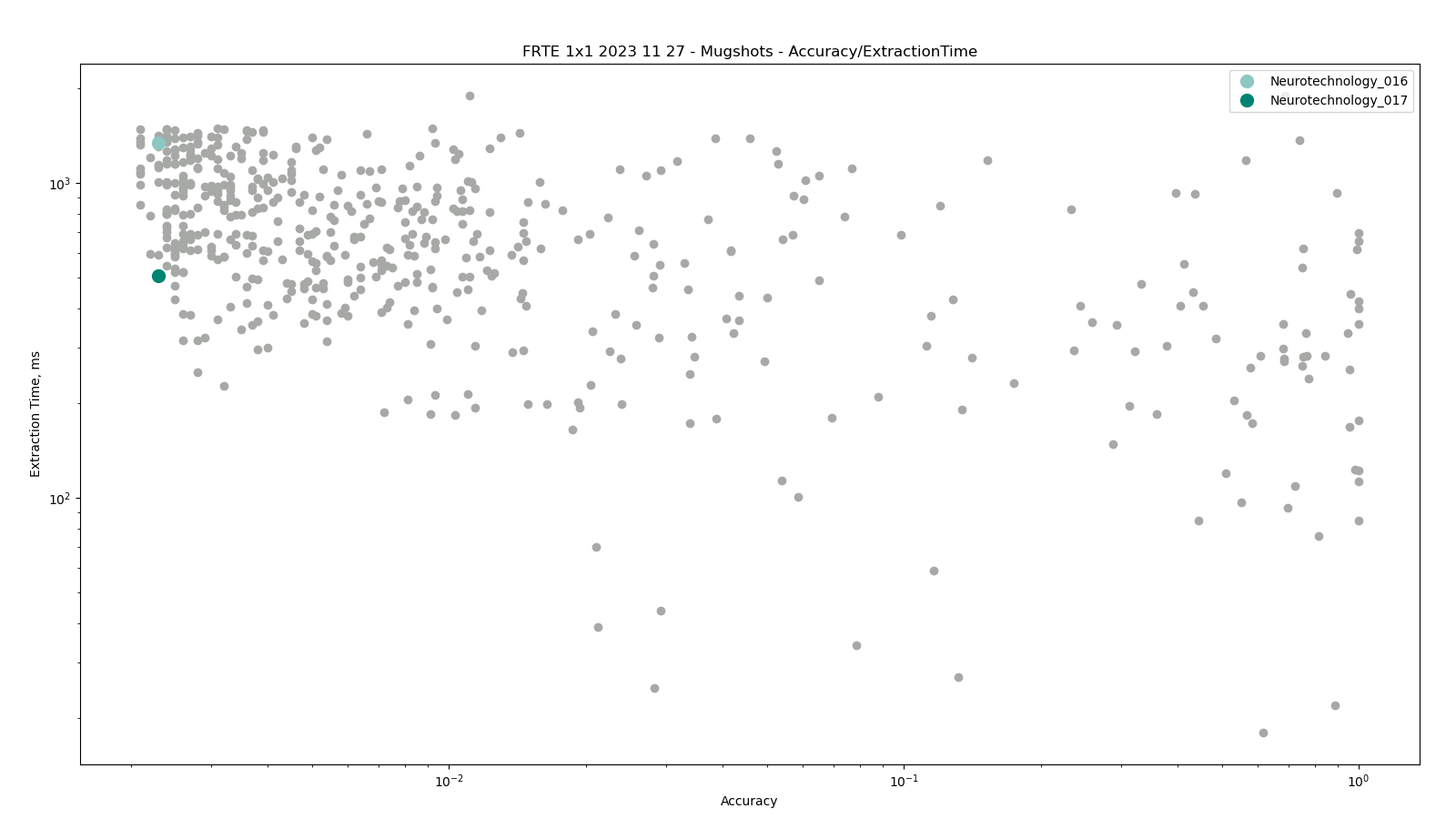
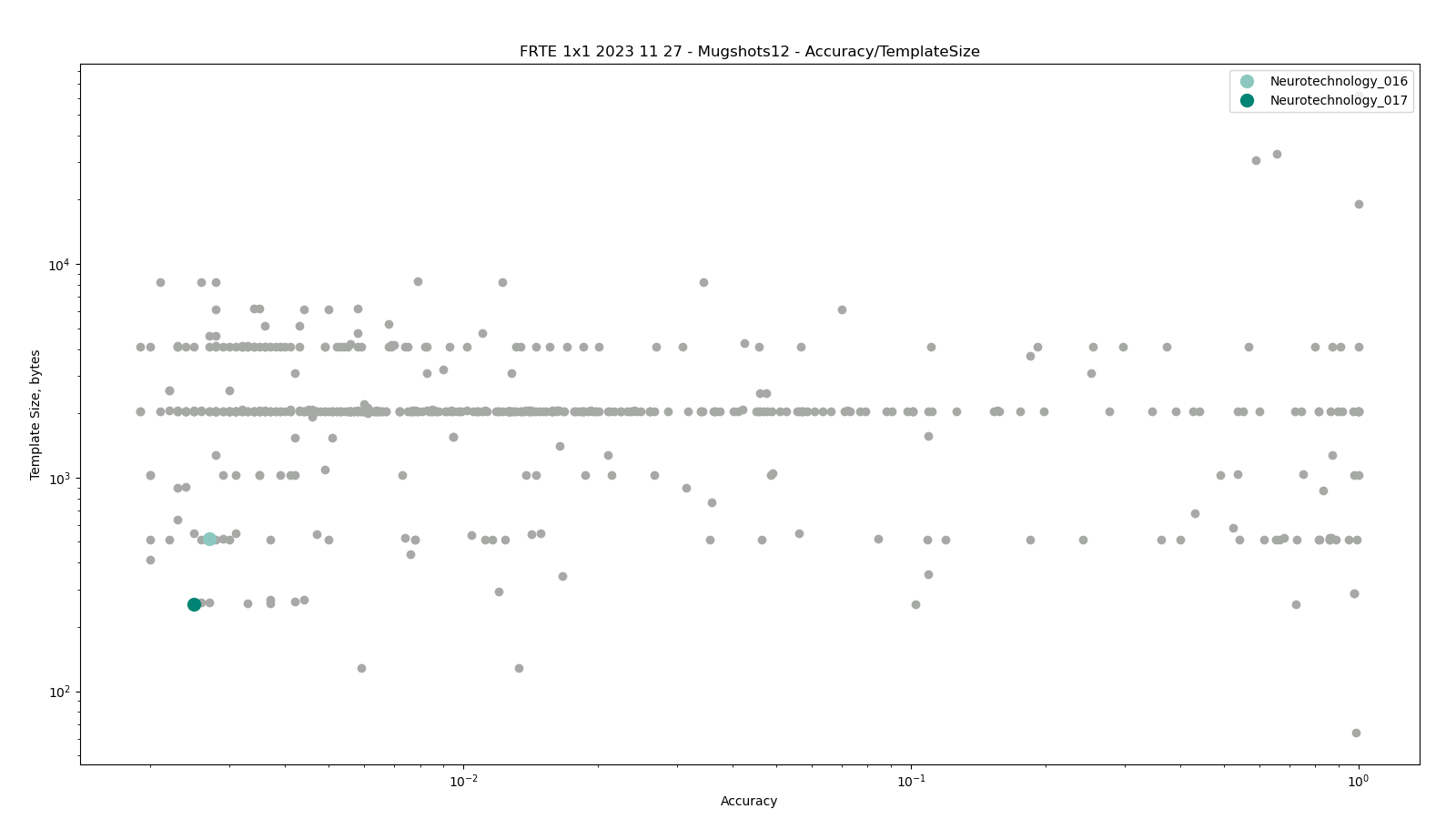
Mugshot
The comparisons were performed between all face templates from the MUGSHOT dataset.
Neurotechnology algorithm accuracy in this scenario was 0.23% FNMR at 0.001% FMR. The most accurate contender showed 0.21% FNMR at the same FMR.
Scenario overview
- One image from the dataset was used to create one face template.
- All face templates were compared between each other.
- Each comparison score was obtained by comparing two different templates (simple one-to-one verification).
- Gender attribute was used to exclude comparisons between different gender subjects.
Accuracy versus performance metrics
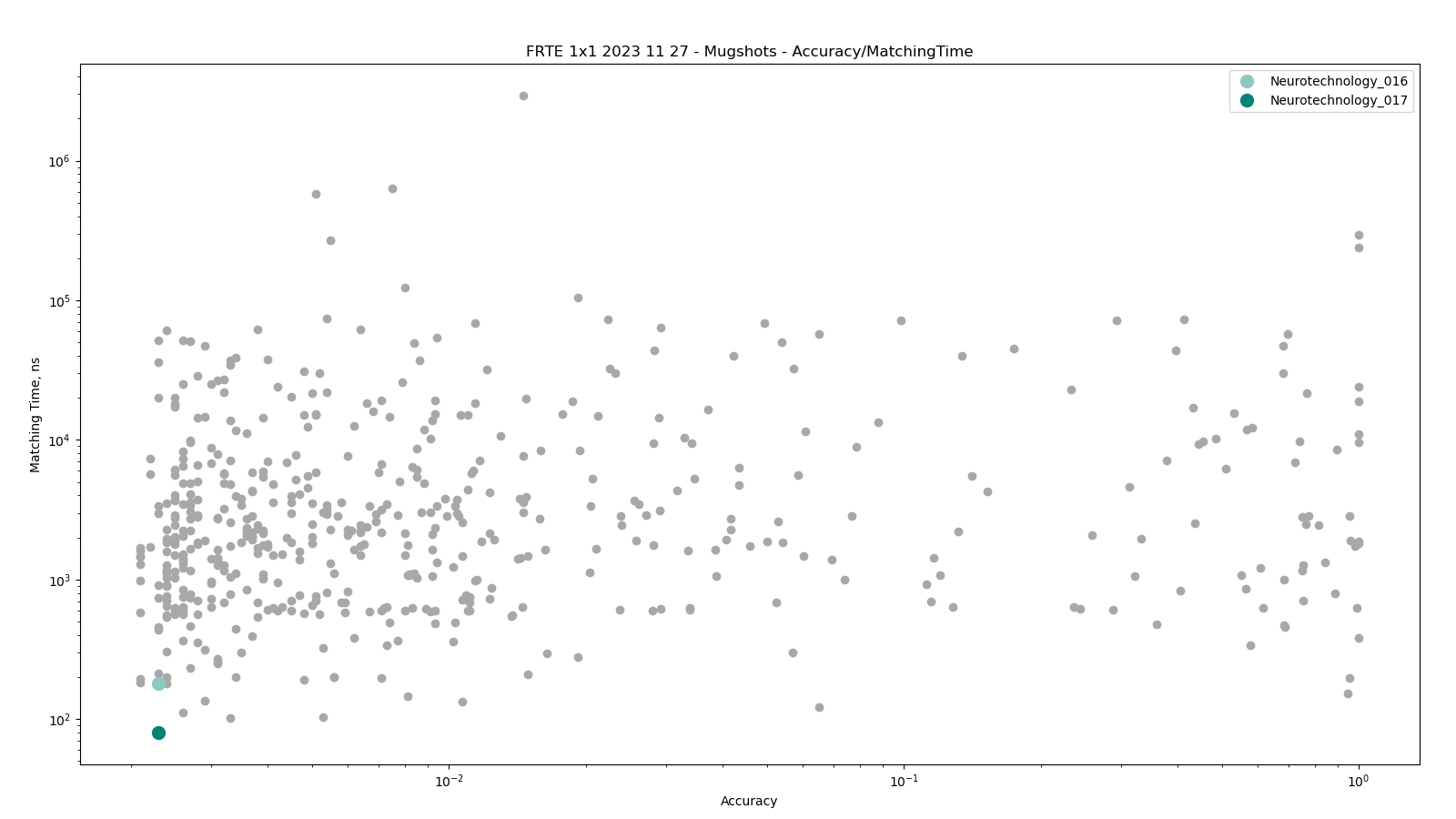
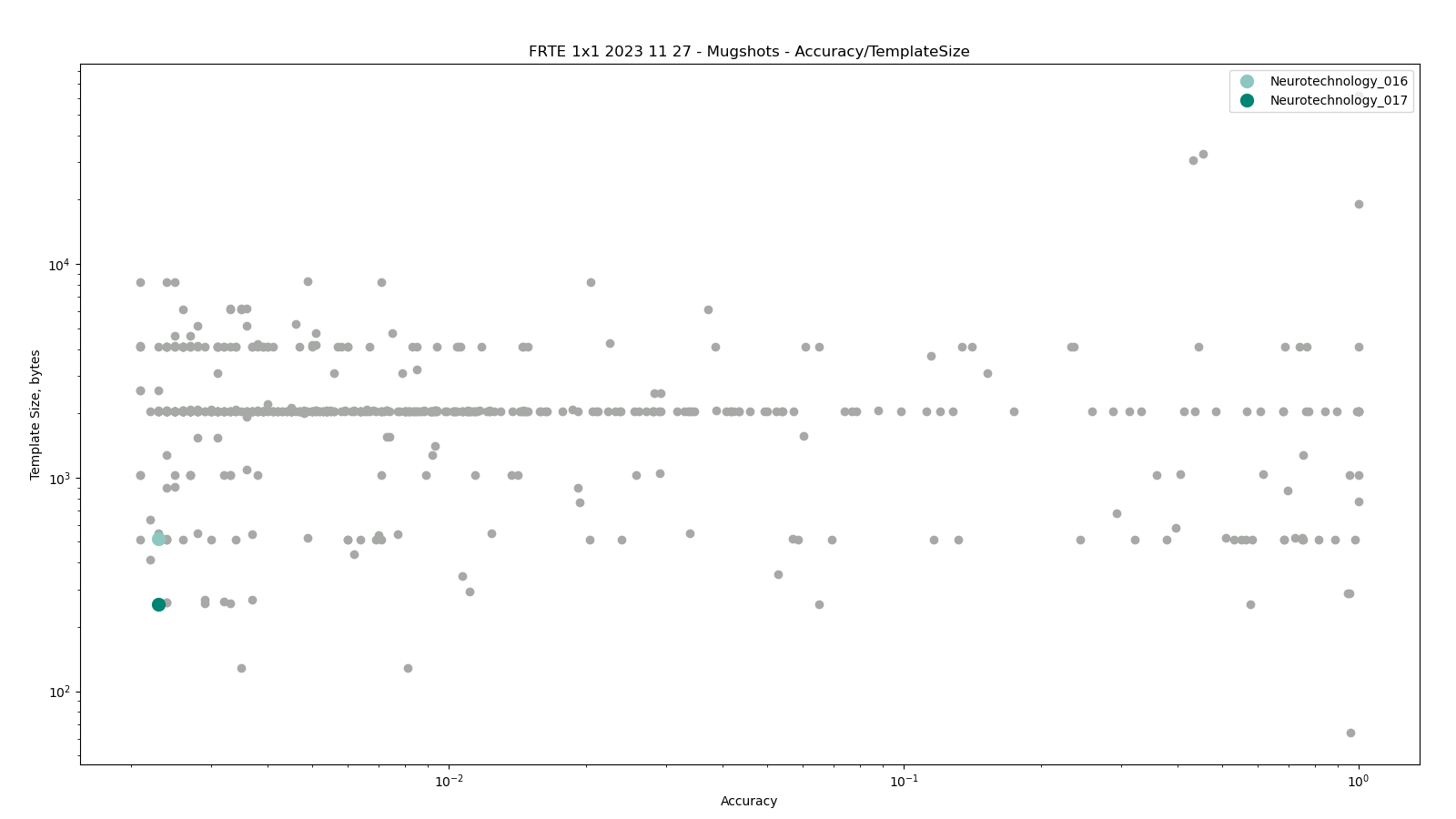
The charts below show the accuracy of all tested algorithms, with the highlighted dots corresponding to the Neurotechnology algorithm submissions.
Click to zoom
Click to zoom
Click to zoom
Mugshots with 12+ years difference
The test was performed using facial templates, generated from the MUGSHOT dataset. The comparisons were performed only between templates representing same or different persons with age difference of 12 or more years between them.
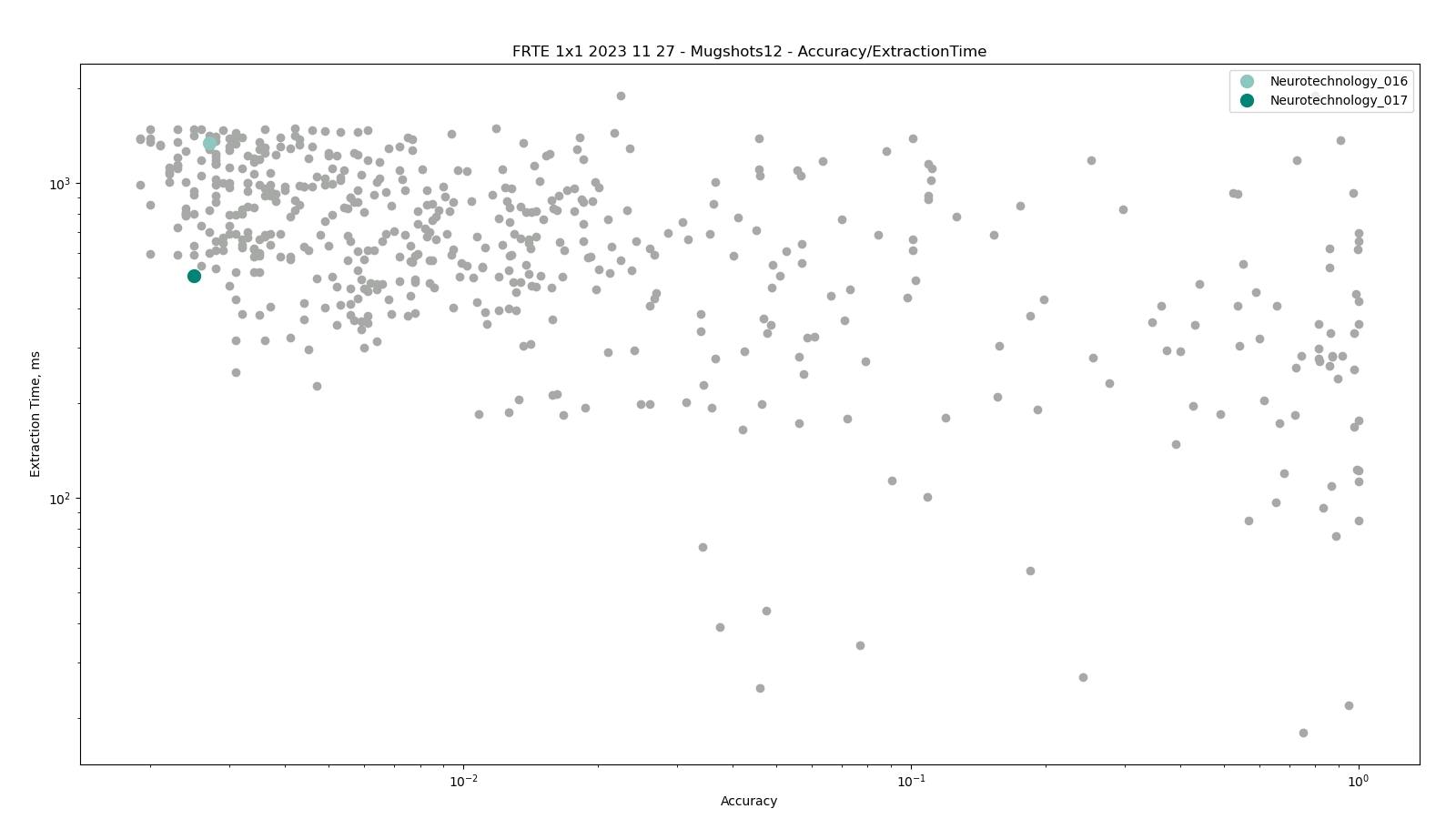
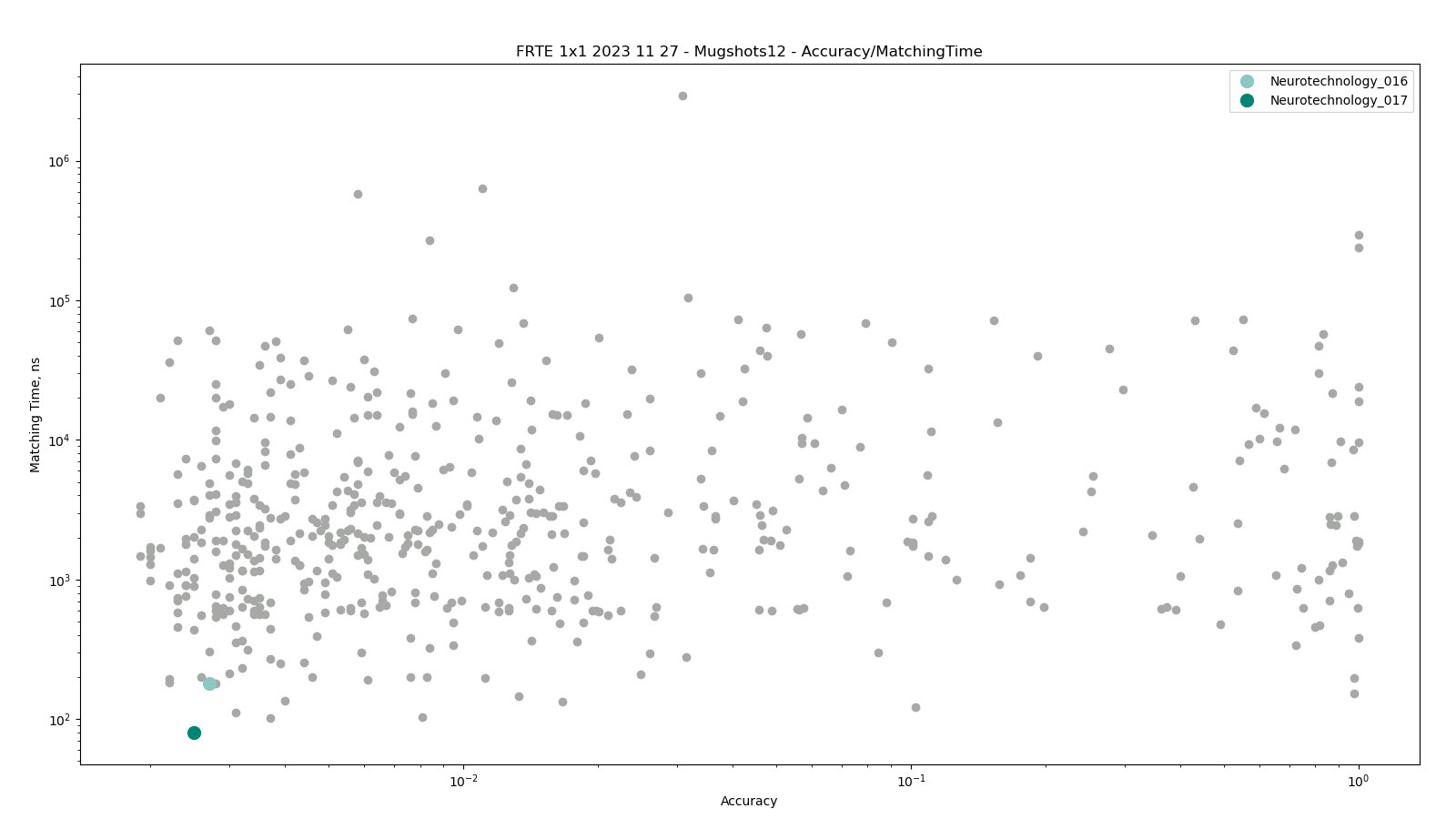
Neurotechnology algorithm accuracy in this scenario was 0.23% FNMR at 0.001% FMR. The most accurate contender showed 0.19% FNMR at the same FMR.
Scenario overview
- One image from the MUGSHOT dataset was used to create one face template.
- Age attribute was used to exclude template pairs, which represented same or different persons with age difference of less than 12 years at the capture moment, from the comparison.
- Gender attribute was used to exclude comparisons between different gender subjects.
- Each comparison score was obtained by comparing two different templates (simple one-to-one verification).
Accuracy versus performance metrics
The charts below show the accuracy of all tested algorithms, with the highlighted dots corresponding to the Neurotechnology algorithm submissions.
Click to zoom
Click to zoom
Click to zoom
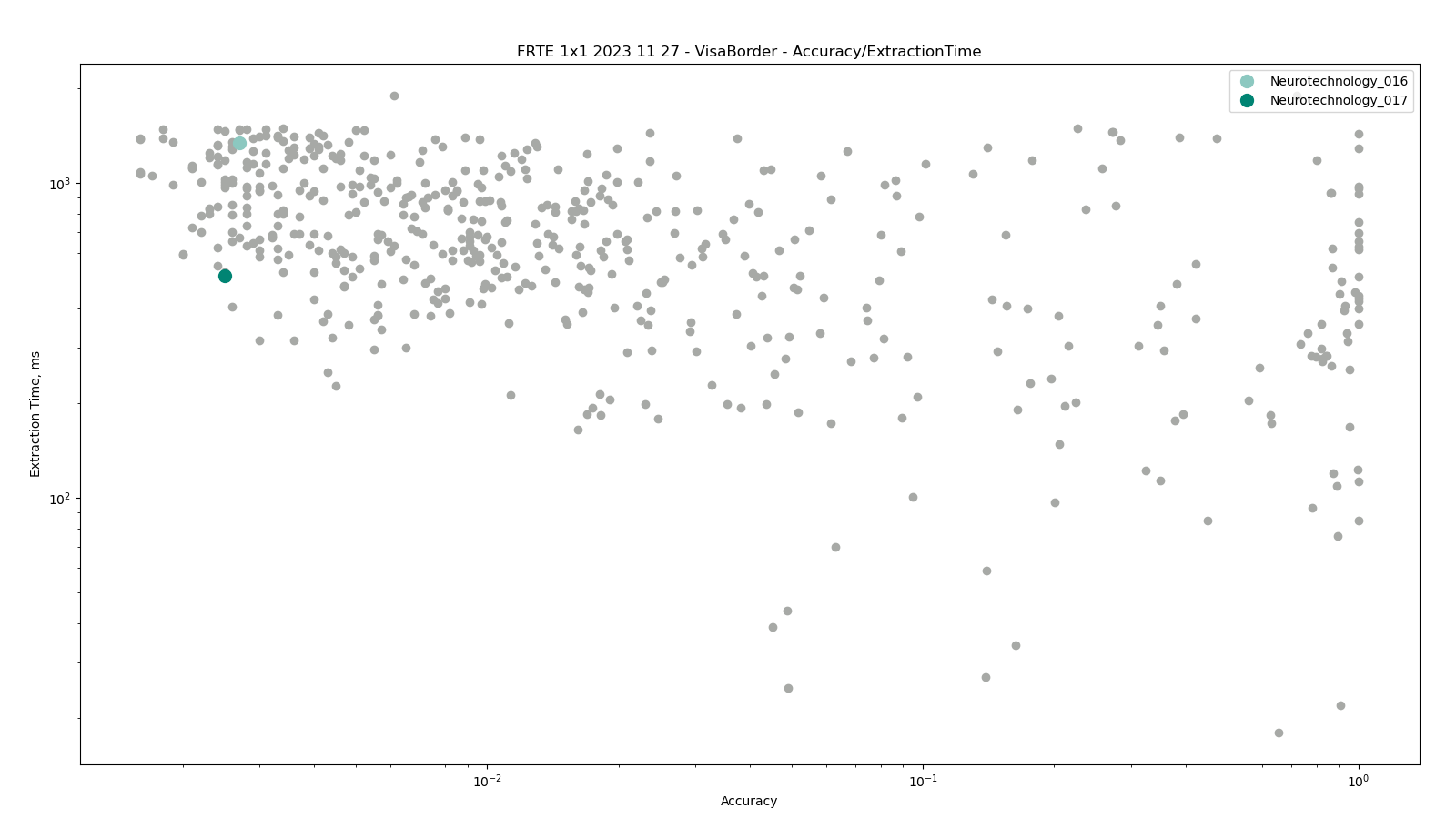
Visa vs Border
The test was performed by comparing high-quality images from the VISA dataset against lower quality images from the BORDER dataset. Both datasets include subjects from more than 100 countries, with specific imbalances due to visa issuance patterns and border-crossing demographics correspondingly.
Neurotechnology algorithm accuracy in this scenario was 0.25% FNMR at 0.0001% FMR. The most accurate contender showed 0.16% FNMR at the same FMR.
Scenario overview
- One image from Visa or Border datasets was used to create one face template.
- Gender attribute was used to exclude comparisons between different gender subjects.
- Each pre-filtered template from the Visa dataset was compared against each pre-filtered template from the Border dataset
- Each comparison score was obtained by comparing two different templates (simple one-to-one verification).
Accuracy versus performance metrics
The charts below show the accuracy of all tested algorithms, with the highlighted dots corresponding to the Neurotechnology algorithm submissions.
Click to zoom
Click to zoom
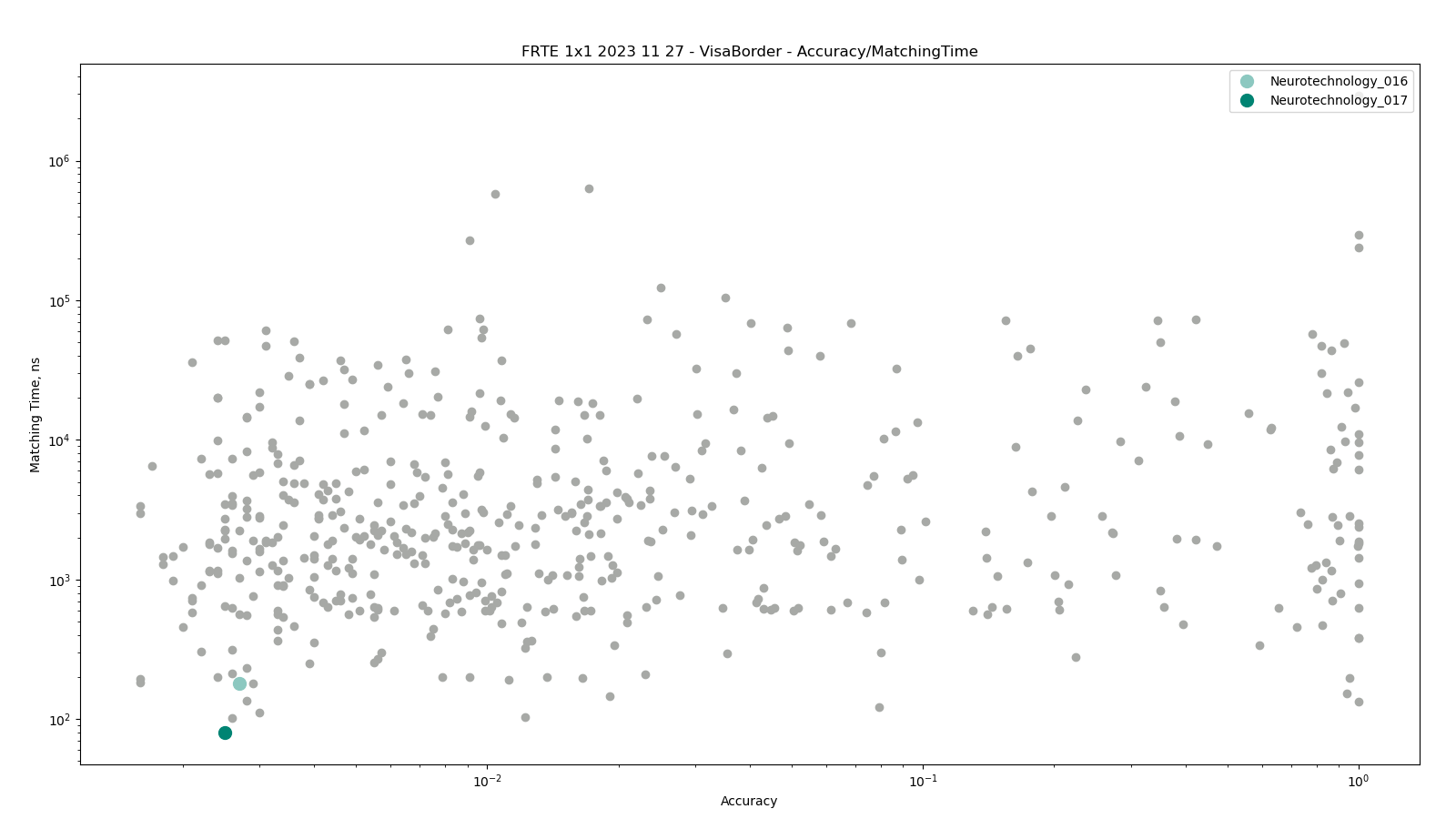
Click to zoom
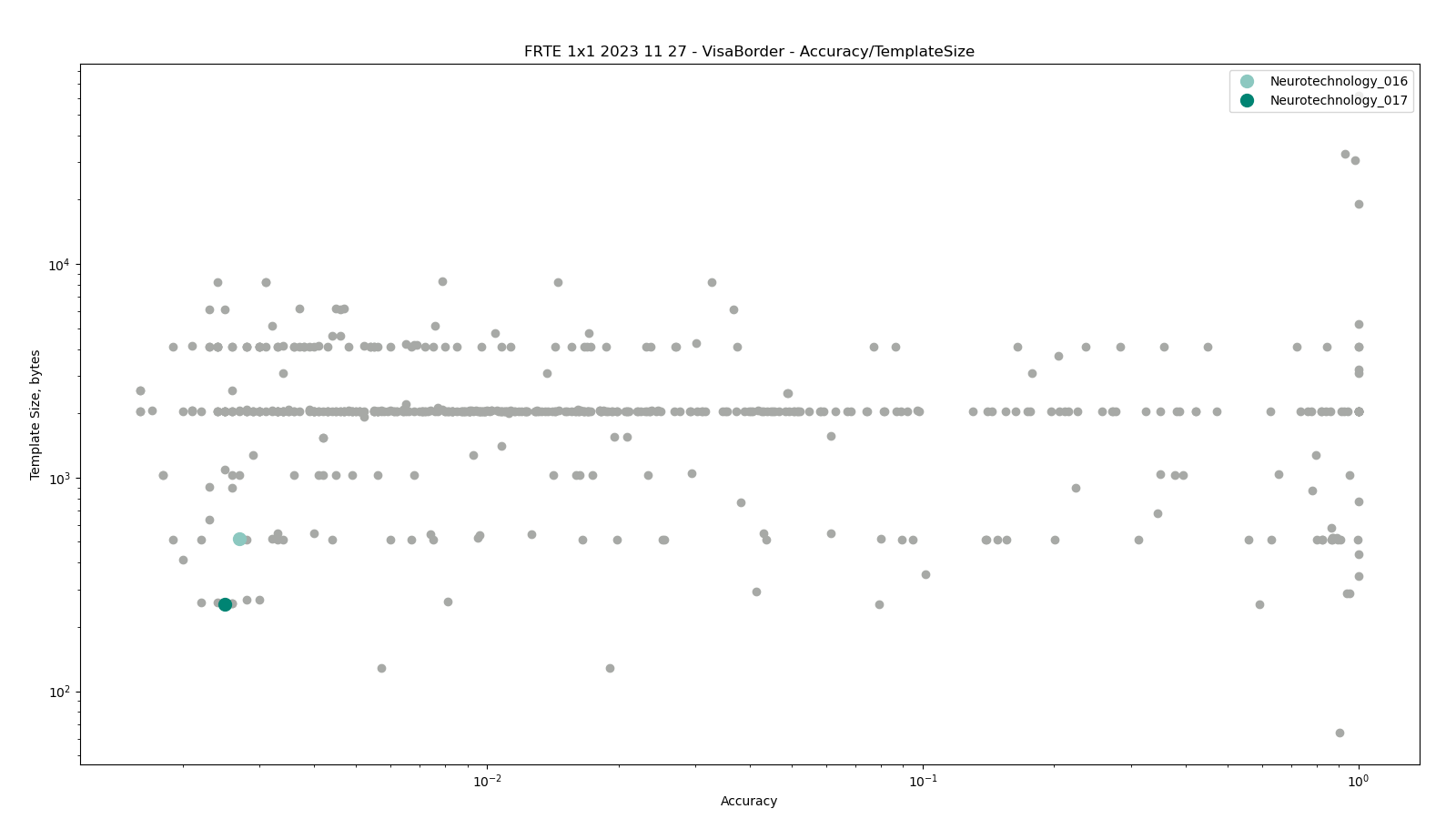
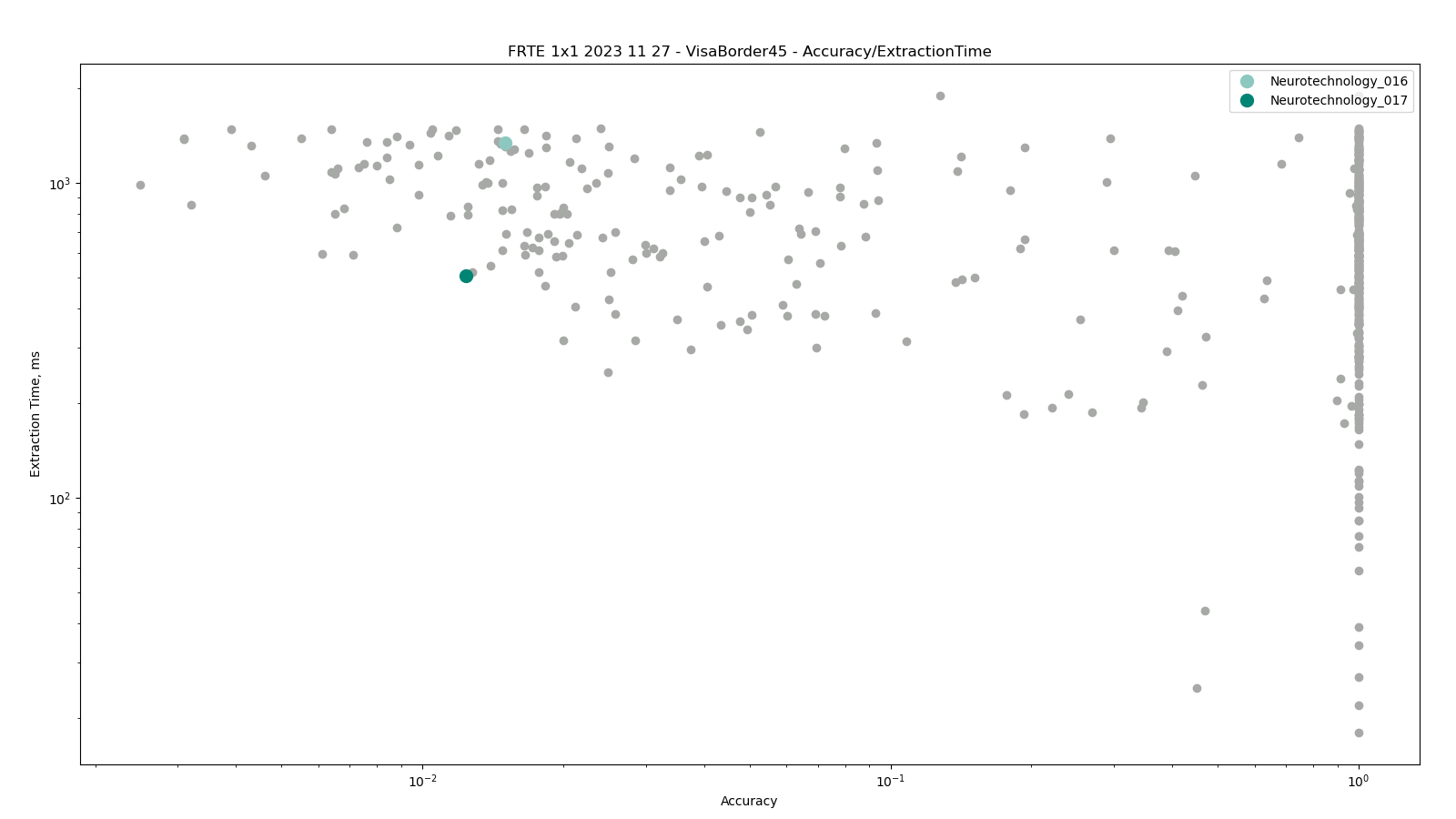
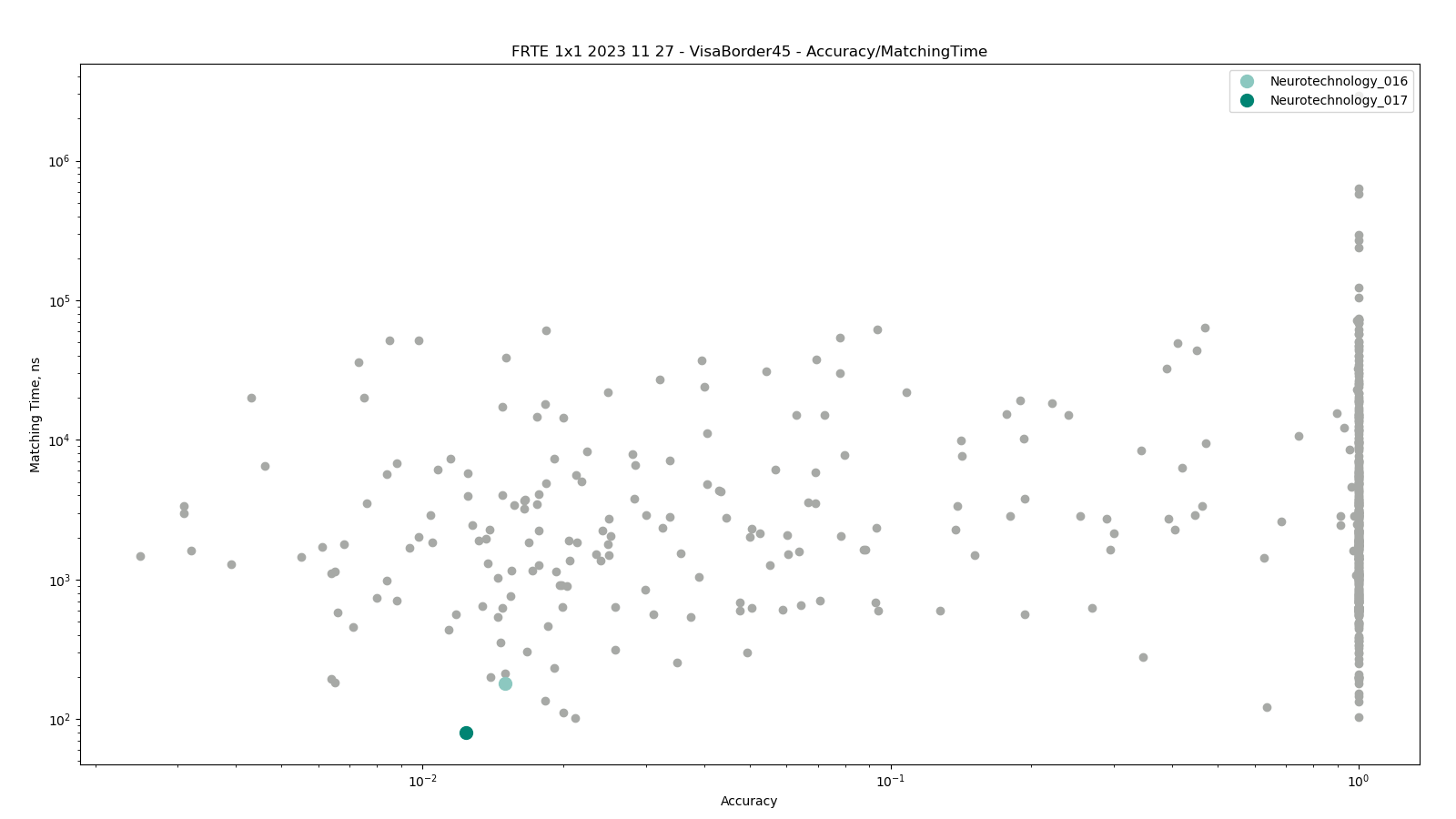
Visa vs Border with 45+ degrees yaw angle difference
The test was performed by comparing high-quality images from the VISA dataset against lower quality images from the BORDER dataset. The comparisons were performed only between photos representing same or different persons with face yaw angle difference of 45 or more degrees between them.
Neurotechnology algorithm accuracy in this scenario was 1.24% FNMR at 0.0001% FMR. The most accurate contender showed 0.25% FNMR at the same FMR.
Scenario overview
- One image from Visa or Border datasets was used to create one face template.
- Gender attribute was used to exclude comparisons between different gender subjects.
- Face yaw angle attribute was used to filter face template pairs for achieving the required yaw angle difference of 45 or more degrees.
- Each pre-filtered template from the Visa dataset was compared against each pre-filtered template from the Border dataset
- Each comparison score was obtained by comparing two different templates (simple one-to-one verification).
Accuracy versus performance metrics
The charts below show the accuracy of all tested algorithms, with the highlighted dots corresponding to the Neurotechnology algorithm submissions.
Click to zoom
Click to zoom
Click to zoom
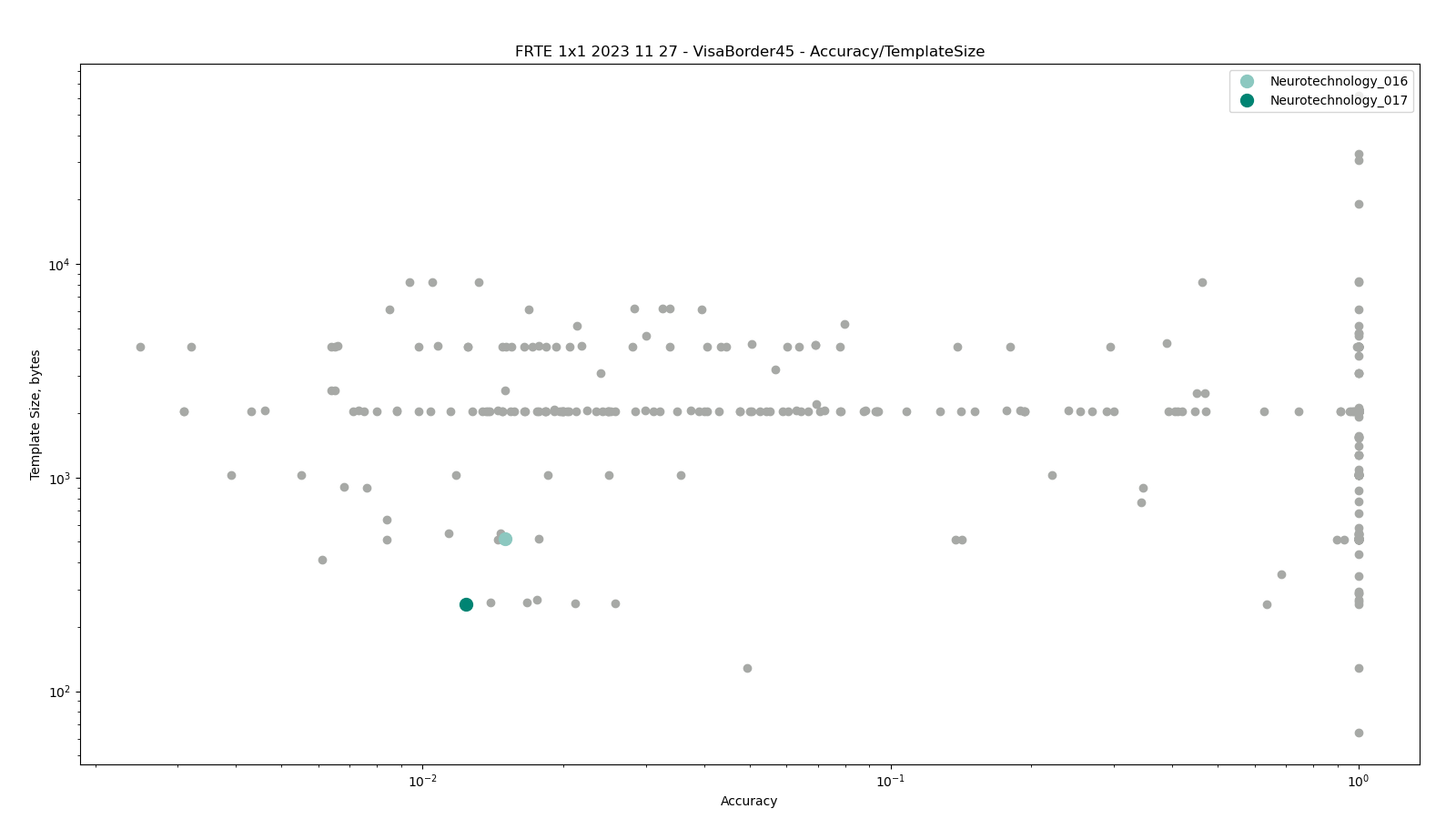
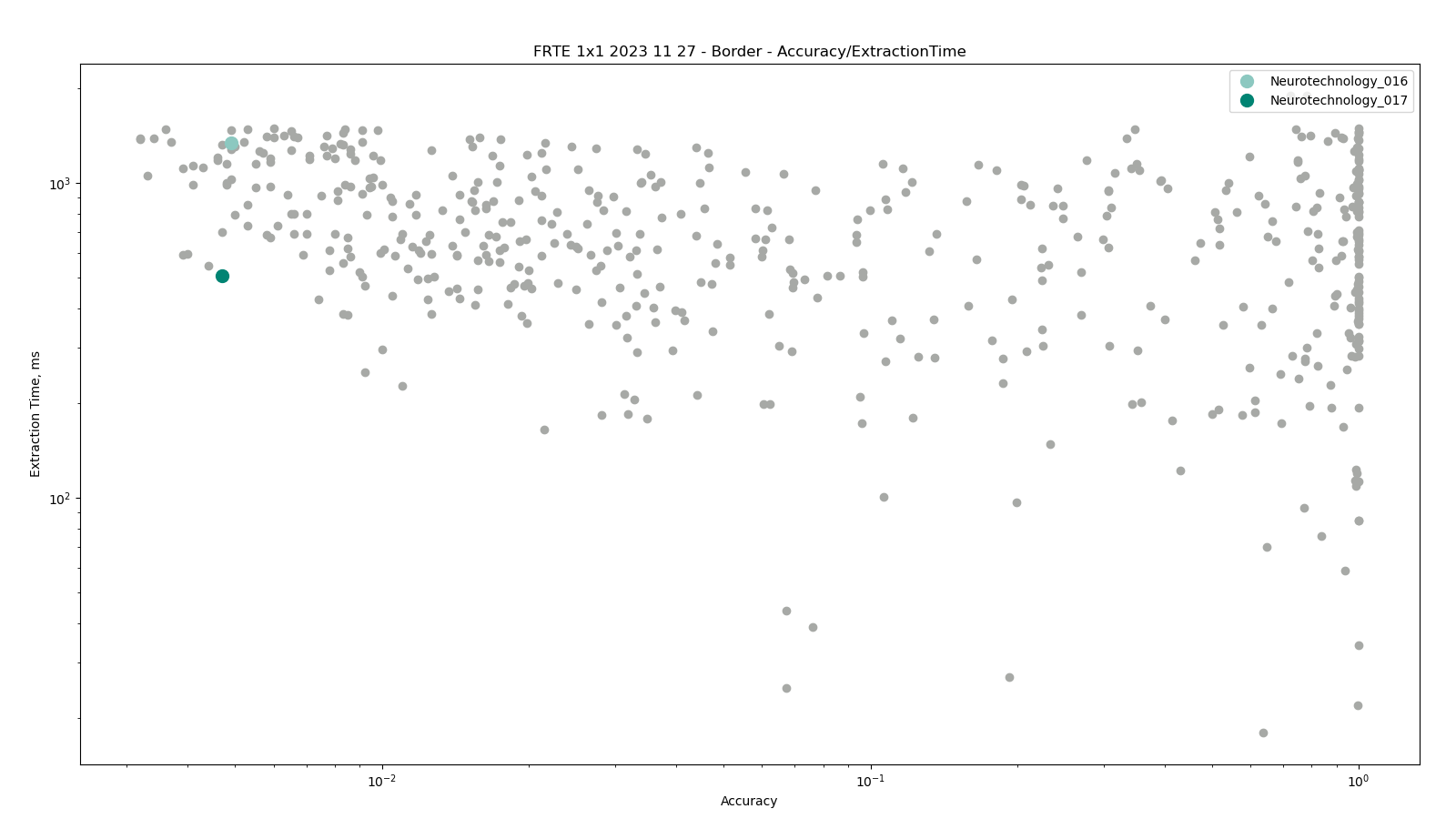
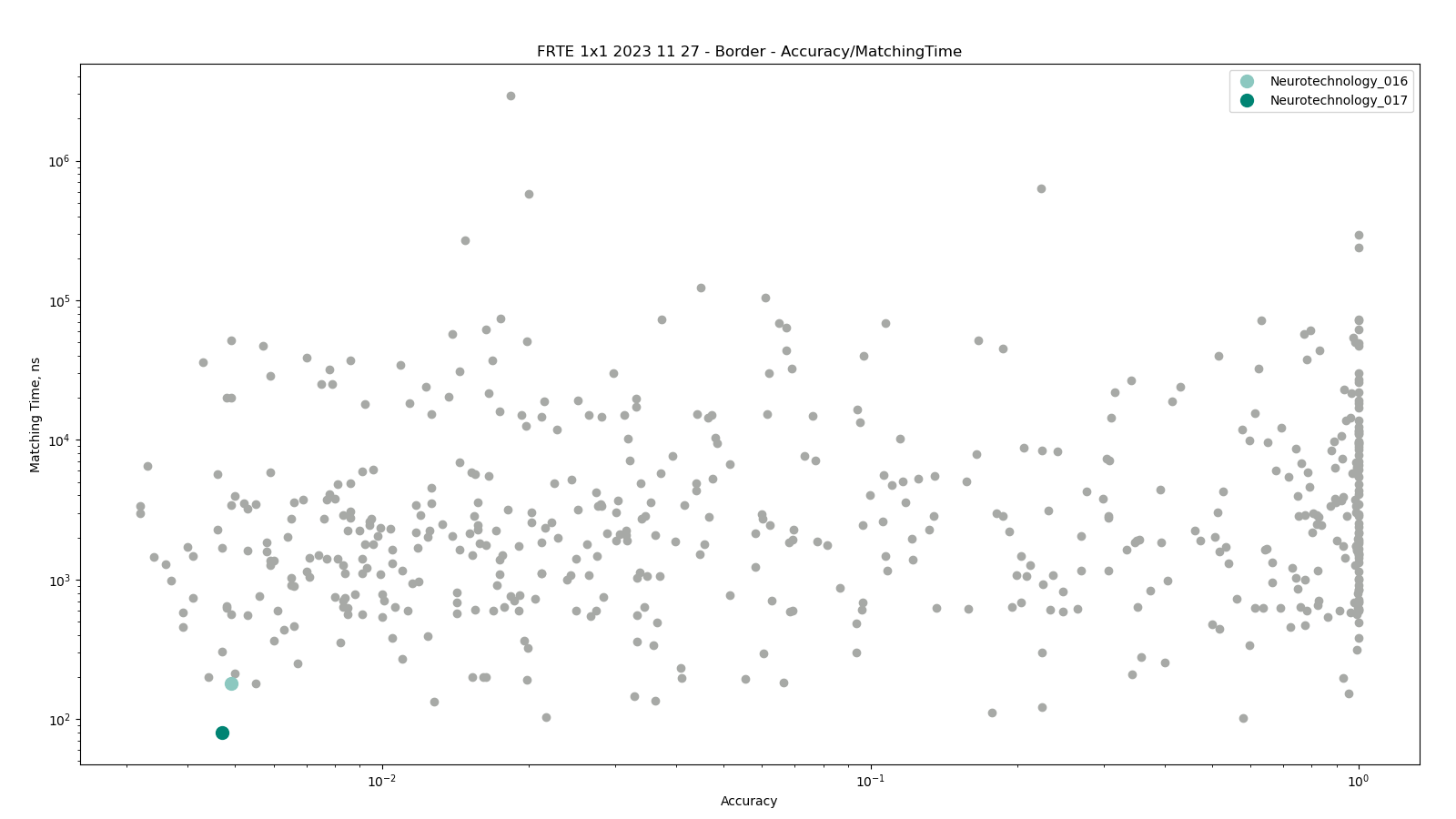
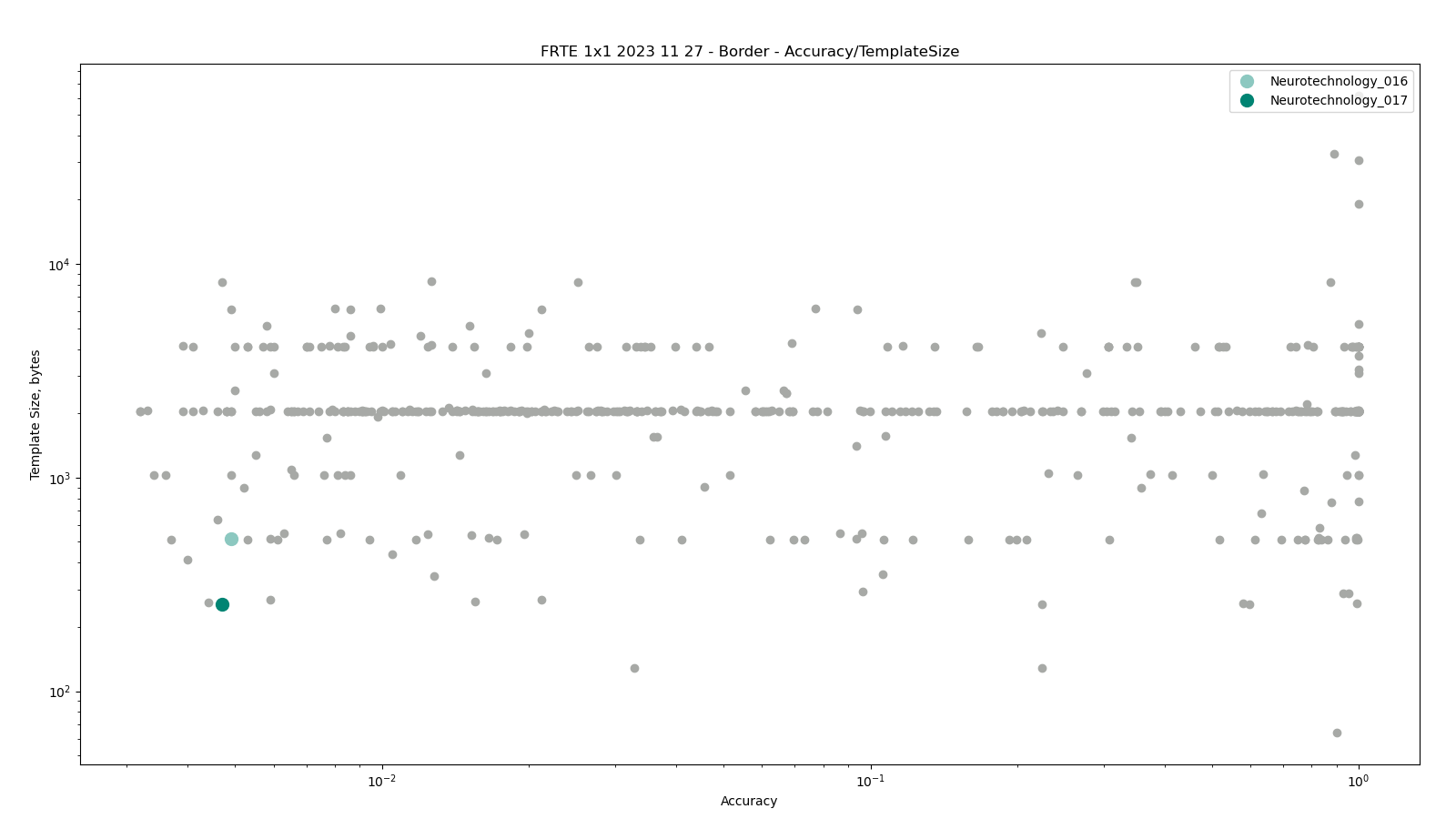
Border
The comparisons were performed between face templates from the MUGSHOT dataset, using gender attribute to exclude comparisons between different gender subjects.
Neurotechnology algorithm accuracy in this scenario was 0.47% FNMR at 0.0001% FMR. The most accurate contender showed 0.32% FNMR at the same FMR.
Scenario overview
- One image from the dataset was used to create one face template.
- Gender attribute was used to exclude comparisons between different gender subjects.
- All pre-filtered face templates were compared between each other.
- Each comparison score was obtained by comparing two different templates (simple one-to-one verification).
Accuracy versus performance metrics
The charts below show the accuracy of all tested algorithms, with the highlighted dots corresponding to the Neurotechnology algorithm submissions.
Click to zoom
Click to zoom
Click to zoom
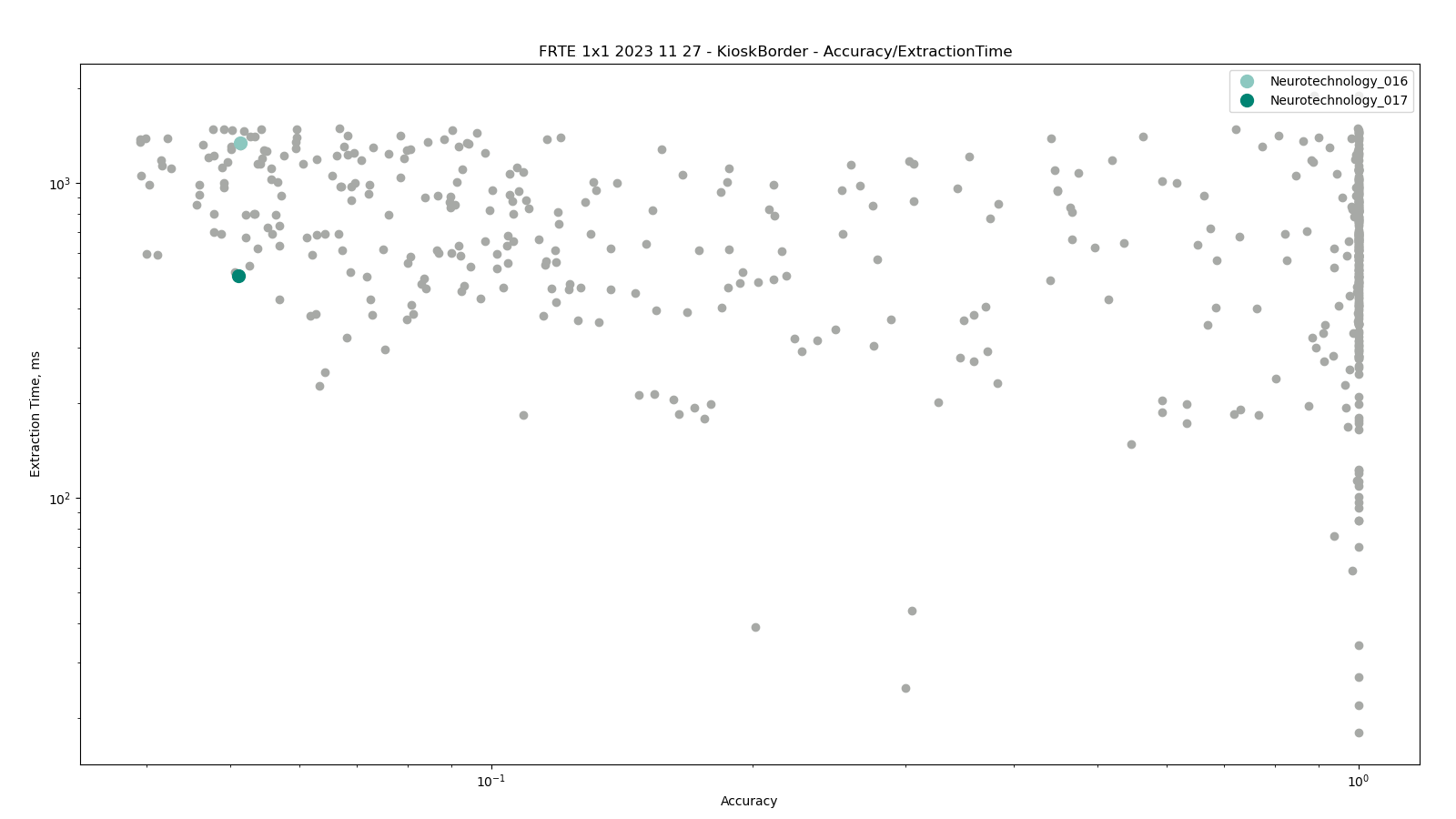
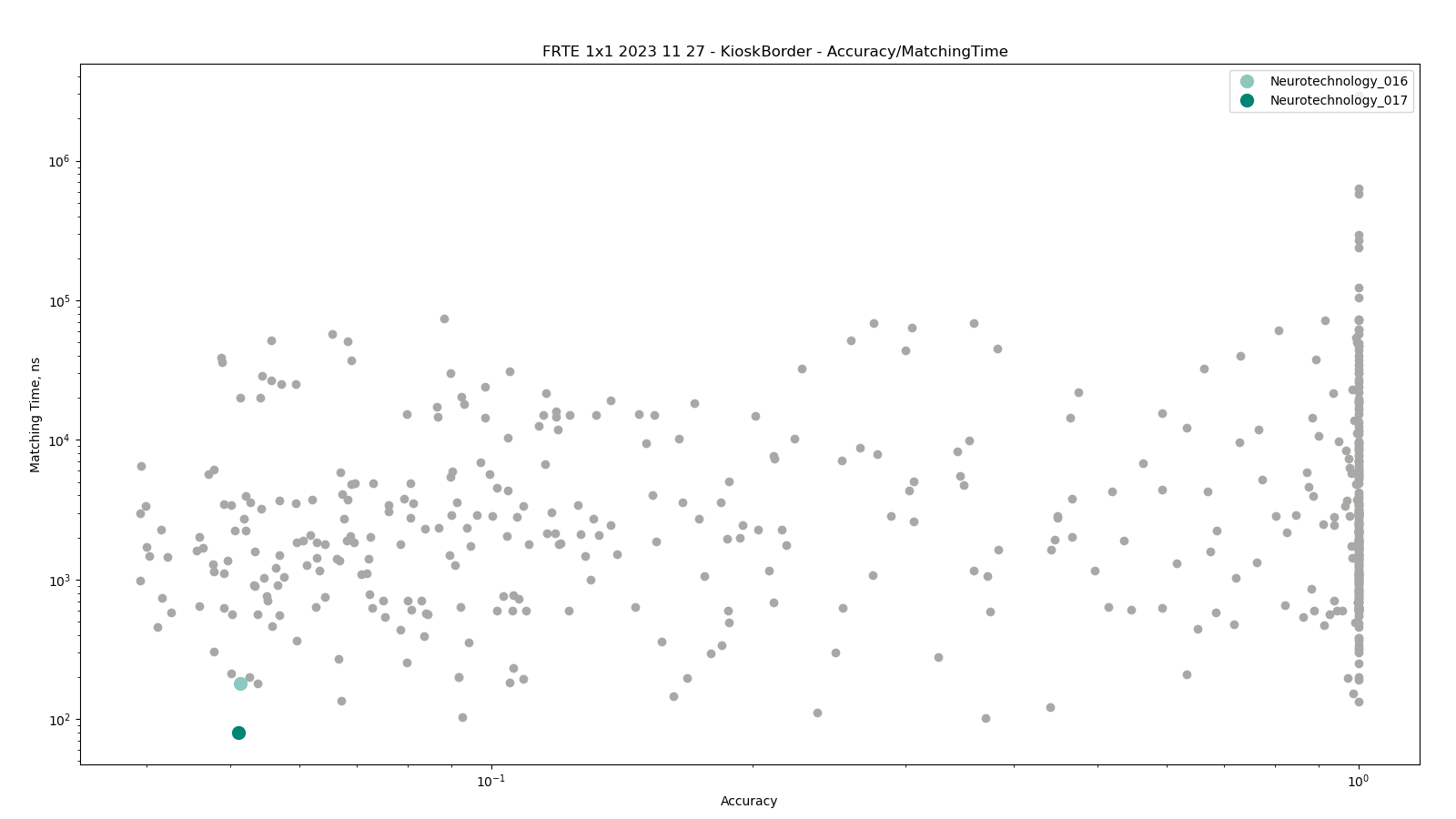
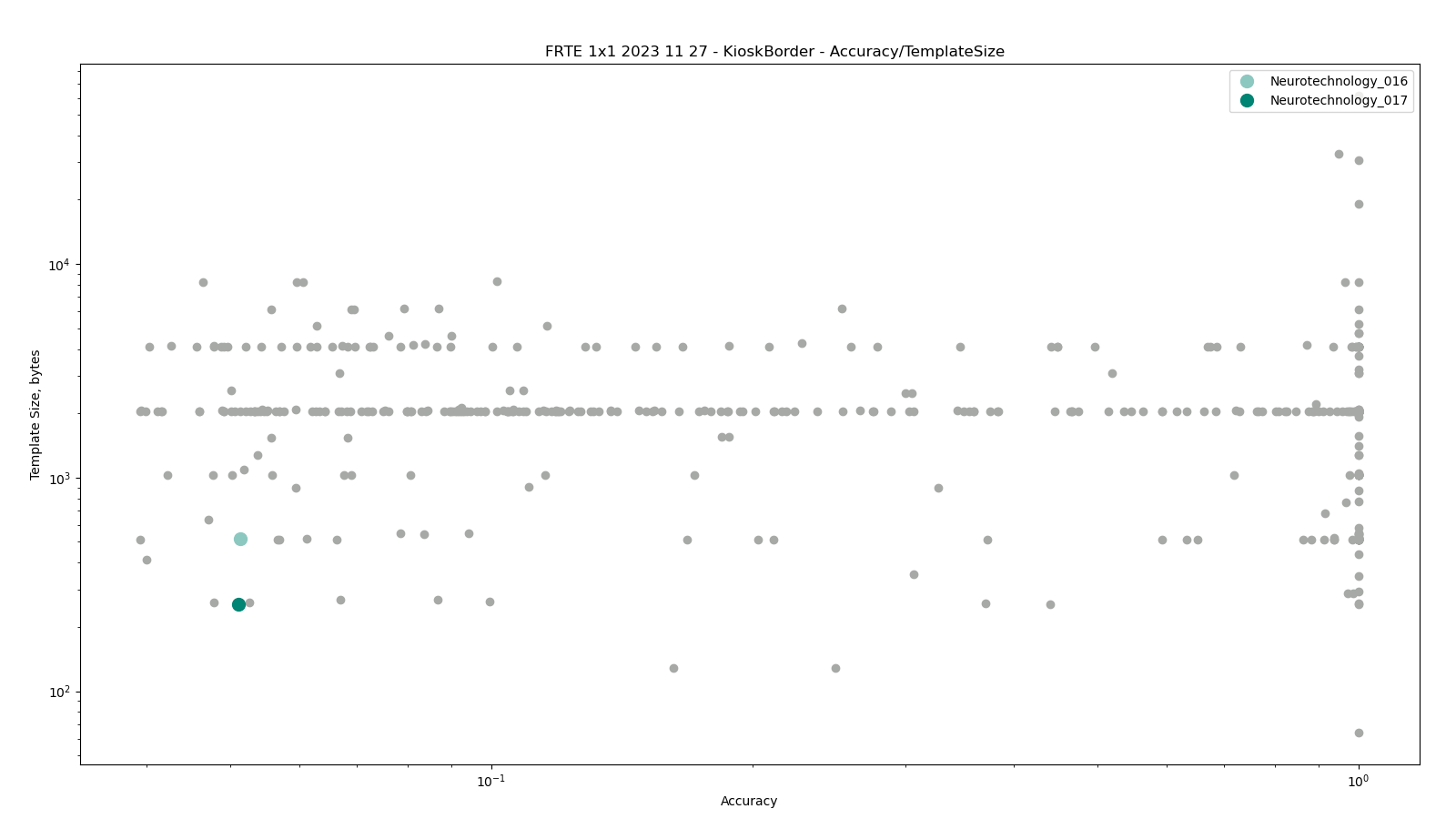
Border vs. Kiosk
The test was performed by comparing higher quality images from the BORDER dataset against lower quality images from the KIOSK dataset. Both datasets include subjects from more than 100 countries, with specific imbalances due to visa issuance patterns and border-crossing demographics correspondingly.
The dataset is made from images. which were captured from cooperating subjects in a partially controlled environment. Images' quality varied due to an automated, non-supervised capture method.
Neurotechnology algorithm accuracy in this scenario was 5.11% FNMR at 0.001% FMR. The most accurate contender showed 3.94% FNMR at the same FMR.
- One image from each dataset was used to create one face template.
- Gender attribute was used to exclude comparisons between different gender subjects.
- All pre-filtered face templates from one dataset were compared with all pre-filtered templates from the other dataset.
- Each comparison score was obtained by comparing two different templates (simple one-to-one verification).
- The comparisons were fully zero-effort, meaning there was no pre-grouping by gender, age or other covariates.
Accuracy versus performance metrics
The charts below show the accuracy of all tested algorithms, with the highlighted dots corresponding to the Neurotechnology algorithm submissions.
Click to zoom
Click to zoom
Click to zoom
Datasets Summary
VISA dataset
The dataset represents typical photos of US visa applicants. According to the dataset description, the face images are generally high quality. Part of the images are live capture and the other part is photographed from paper photos.
- More than 100,000 unique persons.
- Part of the images are live capture and part are digitized paper photos.
- High quality images, with conformance with the ISO/IEC 19794-5 Full Frontal image type. Subjects' pose is generally excellent.
- Image size: 252x300 pixels.
- Interocular distance (IOD): 69 pixels.
- Subjects from more than 100 countries are represented, with significant imbalance due to visa issuance patterns.
- All ages are represented, including children, with imbalance due to visa issuance demand.
MUGSHOT dataset
The dataset represents typical photos of suspects taken by law enforcement officers. The photos were taken in a controlled environment thus their quality is high.
- More than 1,000,000 unique persons.
- All images were live capture.
- High quality images, with conformance with the ISO/IEC 19794-5 Full Frontal image type. Subjects' pose is generally excellent.
- Variable image sizes.
- Interocular distance (IOD): from 34 to 297 pixels, with 113 pixels mean and 105 pixels median values.
- All subjects are from the United States.
- All subjects are adults.
Border dataset
The dataset is made of images obtained at border crossing. Images are taken by operators with webcams oriented towards cooperating subjects. The quality of the images may vary due to time-constrained capture and different illumination conditions.
- More than 1,000,000 unique persons.
- All images were live capture
- Variable image quality. There are role, pitch and yaw angle variations. There is some perspective distortion due to close range images. Background illumination is sometimes strong, so faces may be under-exposed. Some faces are partially cropped.
- Interocular distance (IOD): 38 pixels mean.
- Subjects from more than 100 countries are represented, with significant imbalance due to immigration patterns.
- All subjects are adults, with age distribution imbalance due to immigration patterns.
KIOSK dataset
The dataset is made from images. which were captured from cooperating subjects in a partially controlled environment. Images' quality varied due to an automated, non-supervised capture method.
- All images were live capture.
- Many images have a considerable downward pitch angle.
- In some images, faces are partially cropped.
- Some images have other faces in the background.
