Reliability Tests
The identification reliability is important for large-scale systems. MegaMatcher SDK includes a fused algorithm for fast and reliable identification using several biometric records taken from the same person.
As we do not have any single database with all supported biometric modalities, separate tests with selected modalities were performed for the MegaMatcher biometric engines to demonstrate their reliability and performance with single biometric modalities and combinations of several modalities:
Fingerprint, face and iris matching engines tests
The tests with MegaMatcher biometric fingerprint, face and iris matching engines and fused template matching algorithm were performed using Neurotechnology internal multi-biometric database:
- The database had 7,500 sets of biometric records; each set contained 1 face, 2 irises and 10 fingerprints representing a unique person.
- 1,500 unique persons were represented in the database.
- 5 capture sessions were performed for each person.
The tests were performed with these biometric template types:
- 1 fingerprint record extracted from left index fingerprint image.
- 1 face record.
- 1 iris record extracted from left eye image.
- 2 fingerprint records extracted from same person's left and right index fingerprint images.
- 2 iris records extracted from same person's different eye images.
- 1 fingerprint + 1 face records – left index fingerprint and face taken from the same person.
- 1 face + 1 iris records – left iris and face taken from the same person.
- 1 fingerprint + 1 iris records – left index fingerprint and left iris taken from the same person.
- 1 fingerprint + 1 face + 1 iris records – left index fingerprint, left iris and face taken from the same person.
The biometric engines had these parameters set:
- ±90 degrees fingerprint rotation tolerance value was used for template matching;
- ±15 degrees iris rotation tolerance value was used for template matching.
Receiver operation characteristic (ROC) curves are usually used to demonstrate the recognition quality of an algorithm. ROC curves show the dependence of false rejection rate (FRR) on the false acceptance rate (FAR).
1 Fingerprint Record
These tests were performed:
- Test 1 performed template extraction using maximized speed and minimized template size settings. The template matching used settings, whch correspond the Fingerpint Matcher component. MegaMatcher 2025.1 engine reliability in this test is shown as the red curve on the ROC chart.
- Test 2 performed template extraction using maximized accuracy settings. The template matching used settings, whch correspond the Fingerpint Matcher component. MegaMatcher 2025.1 engine reliability in this test is shown as the blue curve on the ROC chart.
- Test 3 performed template extraction using maximized accuracy settings. The template matching used settings, whch correspond the Fast Fingerpint Matcher component. MegaMatcher 2025.1 engine reliability in this test is shown as the green curve on the ROC chart.
- Test 4 showed reference results of using the latent print recognition engine, which is available in the MegaMatcher Criminal Investigation product. This test resulted in 0% false rejection rate for all false acceptance rate settings, and the reliability in this test is shown as a black dot on the bottom left of the ROC chart. MegaMatcher Criminal Investigation employs an algorithm that prioritizes accuracy in latent print matching and takes into consideration automatically detected latent print feature points as well as the examiner's input. Contact us for more details about the MegaMatcher Criminal Investigation.
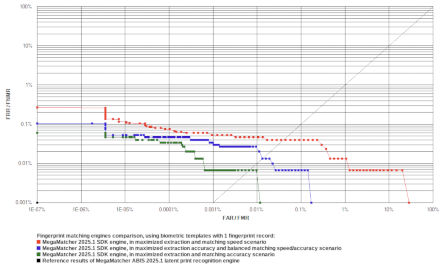
Click to zoom
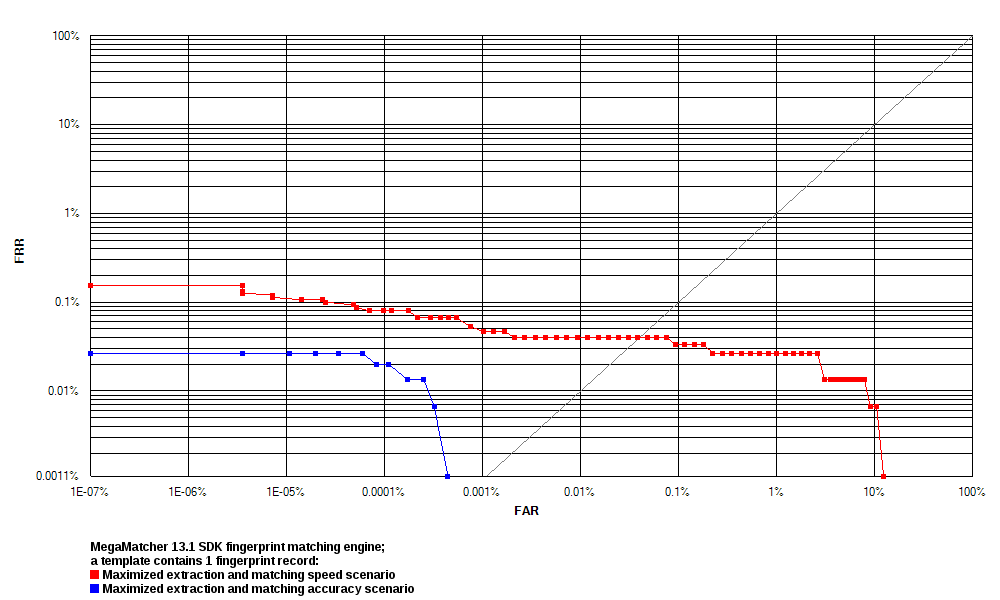
| MegaMatcher 2025.1 fingerprint engine reliability tests | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Test 1 | Test 2 | Test 3 | Test 4 | |||
| FRR at 0.1 % FAR | 0.0400 % | 0.0067 % | 0.0000 % | 0.0000 % | ||
| FRR at 0.01 % FAR | 0.0467 % | 0.0267 % | 0.0067 % | 0.0000 % | ||
| FRR at 0.001 % FAR | 0.0533 % | 0.0333 % | 0.0067 % | 0.0000 % | ||
| FRR at 0.0001 % FAR | 0.0733 % | 0.0467 % | 0.0333 % | 0.0000 % | ||
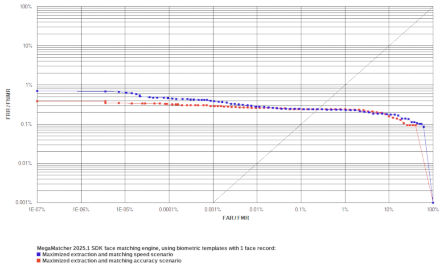
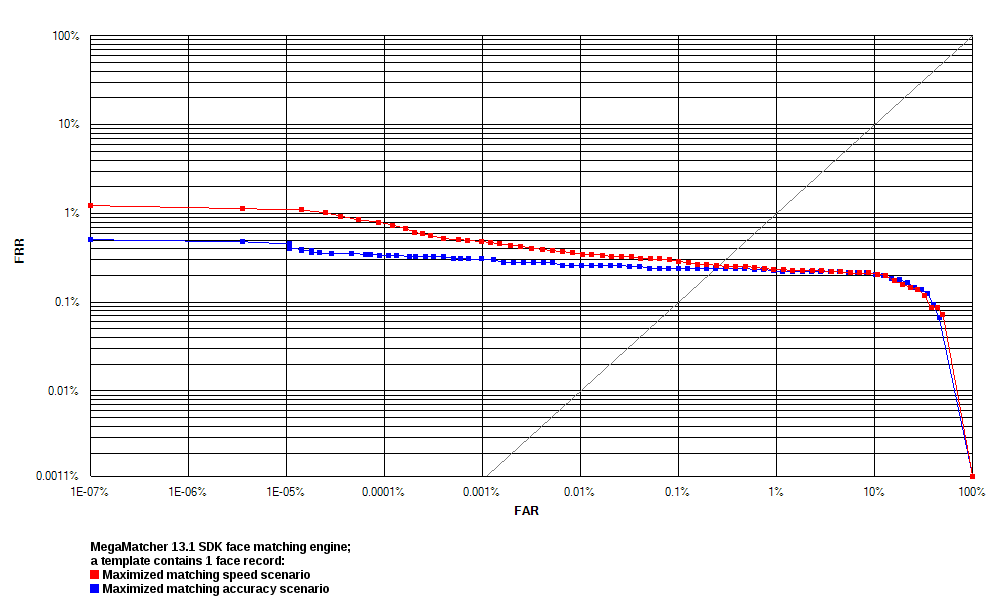
1 Face Record
These tests were performed:
- Test 1 maximized matching speed. MegaMatcher 2025.1 face recognition algorithm reliability in this test is shown as blue curves on the ROC charts.
- Test 2 maximized matching accuracy. MegaMatcher 2025.1 face recognition algorithm reliability in this test is shown as red curves on the ROC charts.
| MegaMatcher 2025.1 face engine reliability tests | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Test 1 | Test 2 | |||||
| FRR at 0.1 % FAR | 0.2467 % | 0.2400 % | ||||
| FRR at 0.01 % FAR | 0.2800 % | 0.2600 % | ||||
| FRR at 0.001 % FAR | 0.3933 % | 0.2867 % | ||||
| FRR at 0.0001 % FAR | 0.4600 % | 0.3267 % | ||||
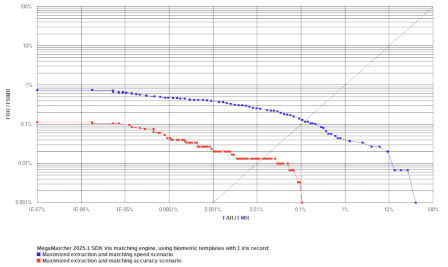
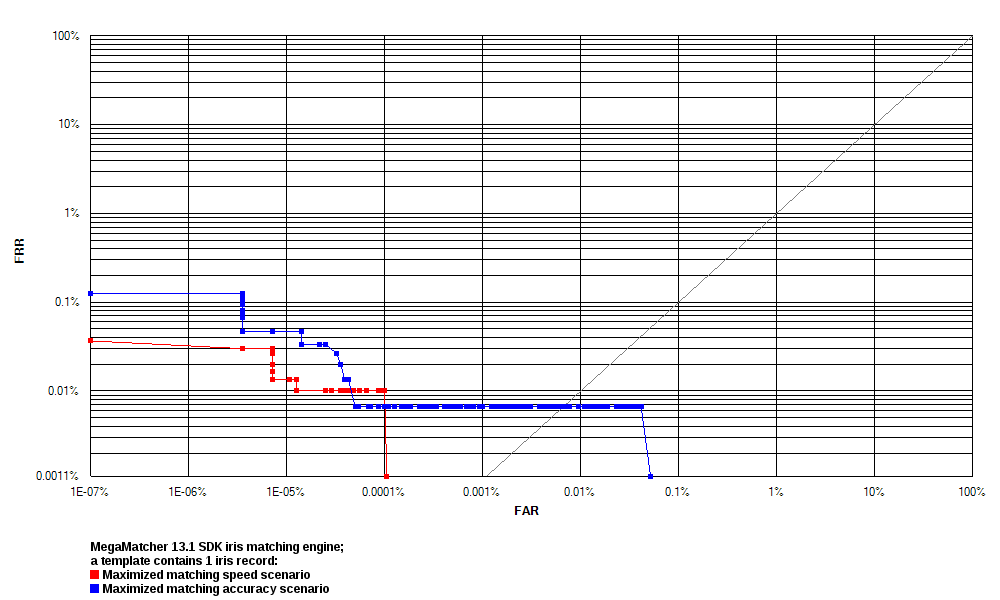
1 Iris Record
These tests were performedssssss:
- Test 1 maximized matching speed. MegaMatcher 2025.1 iris recognition algorithm reliability in this test is shown as blue curves on the ROC charts.
- Test 2 maximized matching accuracy. MegaMatcher 2025.1 iris recognition algorithm reliability in this test is shown as red curves on the ROC charts.
| MegaMatcher 2025.1 iris engine reliability tests | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Test 1 | Test 2 | |||||
| FRR at 0.1 % FAR | 0.1400 % | 0.0033 % | ||||
| FRR at 0.01 % FAR | 0.2533 % | 0.0133 % | ||||
| FRR at 0.001 % FAR | 0.3900 % | 0.0233 % | ||||
| FRR at 0.0001 % FAR | 0.4767 % | 0.0433 % | ||||
Multiple Records Combinations
All similar tests resulted with 0 % FRR for all FAR values when these biometric template types were used:
- 2 fingerprint records
- 2 iris records
- 1 fingerprint + 1 face records
- 1 fingerprint + 1 iris records
- 1 face + 1 iris records
- 1 fingerprint + 1 face + 1 iris records
These tests show that a large-scale automated biometric identification system based on MegaMatcher provides high identification reliability when using fused same-biometric (different fingerprints or irises from the same person), and using multi-biometric identification results in a significant reliability increase.
Fingerprint engine tests using contactless slaps versus scanners-captured
The MegaMatcher 2025.1 SDK's slap biometric engine has been tested using three Neurotechnology internal datasets, captured with different devices. All datasets contained biometric data belonging to the same persons, so one dataset could be used as a gallery, and another as a probe. These datasets were used:
- Dataset 1 – four-finger slaps from both left and right hands, captured in a contactless way with Google Puxel 4a (5G) smartphone camera as photos.
- Dataset 2 – left hand four-finger slaps, captured in a contact way with several different fingerprint readers and saved as images
- Dataset 3 – right hand four-finger slaps, captured in a contact way with several different fingerprint readers and saved as images
Four experiments were performed during rhe testing:
- Experiment 1 – all slaps from the Dataset 1 were compared between each other.
- Experiment 2 – the Dataset 1 was used as probe, and the Dataset 2 was used as gallery.
- Experiment 3 – the Dataset 1 was used as probe, and the Dataset 3 was used as gallery.
- Experiment 4 – the Dataset 1 was used as probe, and both Dataset 2 and Dataset 3 were used as gallery.
Receiver operation characteristic (ROC) curves are usually used to demonstrate the recognition quality of an algorithm. ROC curves show the dependence of false rejection rate (FRR) on the false acceptance rate (FAR). The charts below compare the Experiment 1 results with the results of other experiments.
Click to zoom
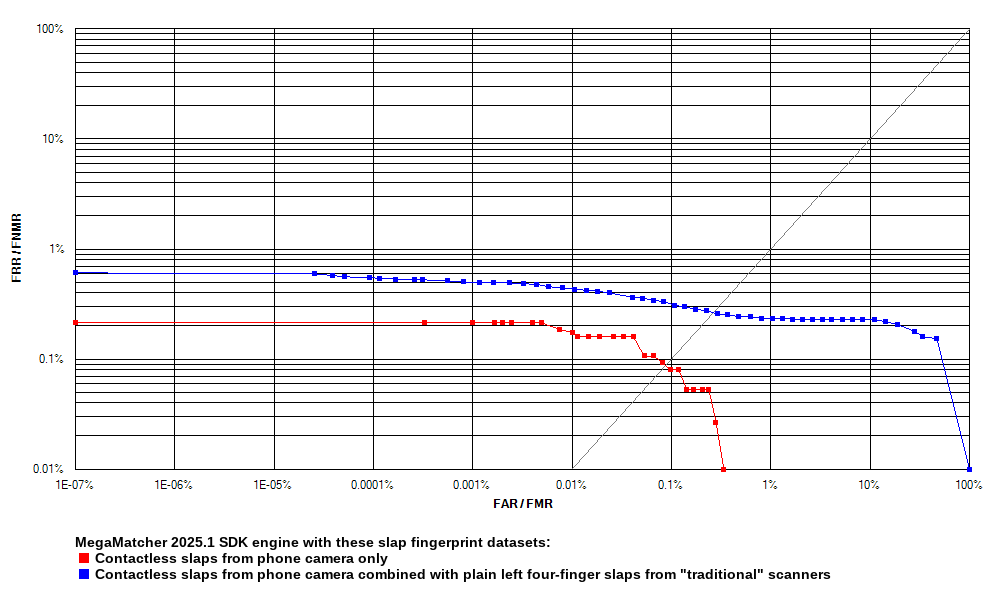
Click to zoom
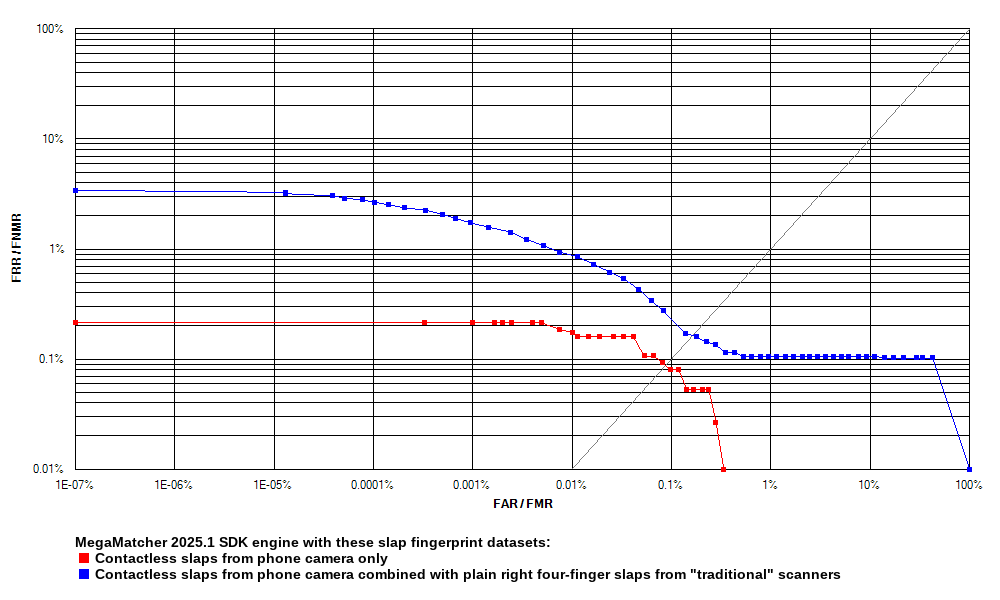
Click to zoom
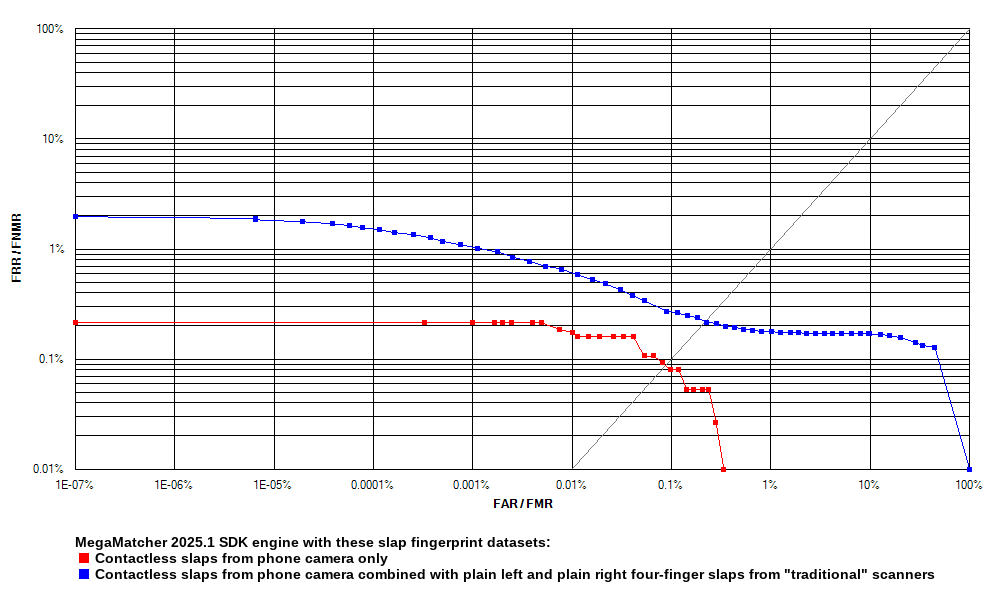
| MegaMatcher 2025.1 SDK fingerprint engine reliability tests using contactless capture | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Experiment 1 | Experiment 2 | Experiment 3 | Experiment 4 | |||
| Genuine pairs | 7,506 | 26,859 | 24,469 | 51,328 | ||
| Impostor pairs | 607,934 | 7,732,866 | 7,732,116 | 15,464,982 | ||
| EER | 0.0869 % | 0.2496 % | 0.1548 % | 0.2095 % | ||
| FRR at 1 % FAR | 0.0000 % | 0.2346 % | 0.1063 % | 0.1773 % | ||
| FRR at 0.1 % FAR | 0.0799 % | 0.3314 % | 0.2738 % | 0.2728 % | ||
| FRR at 0.01 % FAR | 0.1865 % | 0.4431 % | 0.9359 % | 0.6566 % | ||
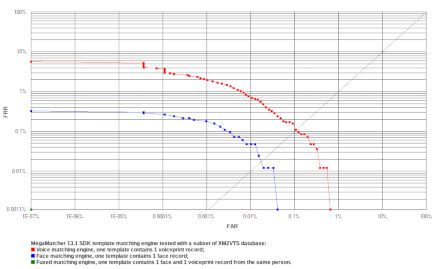
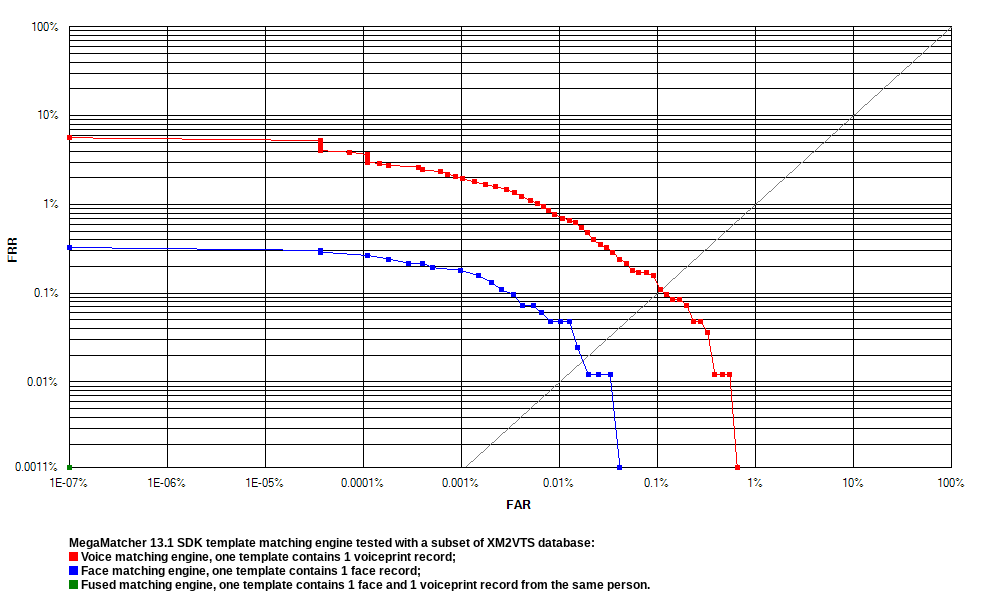
Voiceprint and face matching engines tests
The tests with MegaMatcher biometric face and voiceprint matching engines, and the fused template matching algorithm were performed using face images and voice samples from the XM2VTS Database:
- 295 unique persons were represented in the database.
- 8 capture sessions were performed for each person.
- The phrase 1 from the database was used for the testing, meaning that the same fixed phrase was used for all subjects.
The tests were performed with these biometric template types:
- 1 face record.
- 1 voiceprint record.
- 1 voiceprint + 1 face records taken from the same person.
Receiver operation characteristic (ROC) curves are usually used to demonstrate the recognition quality of an algorithm. ROC curves show the dependence of false rejection rate (FRR) on the false acceptance rate (FAR).
| MegaMatcher 2025.1 face, voiceprint and fused template matching engines tests | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 face in a template |
1 voiceprint in a template |
1 voiceprint + 1 face in a template |
|
| FRR at 0.1 % FAR | 0.0000 % | 0.1575 % | 0.0000 % |
| FRR at 0.01 % FAR | 0.0000 % | 0.7634 % | 0.0000 % |
| FRR at 0.001 % FAR | 0.0848 % | 2.0840 % | 0.0000 % |
| FRR at 0.0001 % FAR | 0.1333 % | 3.8770 % | 0.0000 % |
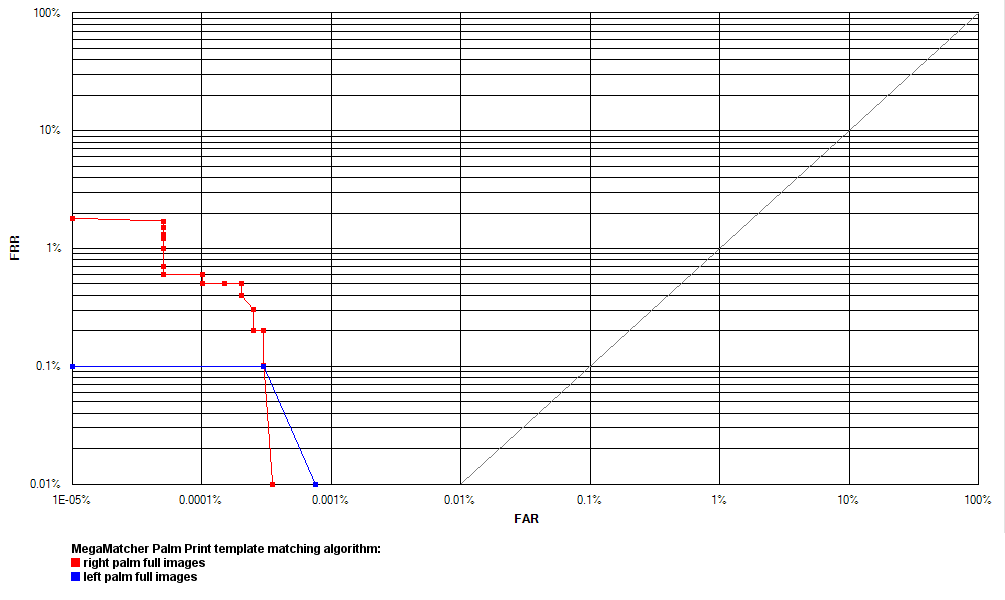
Palm print engine tests
The MegaMatcher palm print template matching algorithm reliability tests were performed using internal palm print images database. The database contained 1,993 images of right hand full palms and 1,996 images of left hand full palms. The database represented 1,000 unique persons.
Receiver operation characteristic (ROC) curves are usually used to demonstrate the recognition quality of an algorithm. ROC curves show the dependence of false rejection rate (FRR) on the false acceptance rate (FAR). The chart with ROC curves for the MegaMatcher palm print template matching algorithm are available on the right.